| IndyWatch Health Watch Feed Archiver | |
 |
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day |
|
IndyWatch Health Watch Feed was generated at Community Resources IndyWatch. |
|
Saturday, 24 June
00:04
Tucker Carlson June 22 2023 on the Hatred of Candidate Kennedy Age of Autism The Rebel Alliance!
Anne Dachel has transcribed Tucker Carlson's Tucker on Twitter June 22, 2023
comments on Candidate Kennedy and Dr. Peter Hotez for posterity.
Posterity in this case is not "future generations," but anyone who
tries to find the YouTube video, which will surely be taken down
soon. Isn't Anne Dachel the GREATEST?
June 22, 2023, Tucker Carlson 6/22/23 Ep. 6
Theres never been a candidate for President the media hated more Robert F. Kennedy, Jr.
You thought that title belonged to Donald Trump. Of course, it must. But go check the coverage.
Trump got a gentle scalp massage by comparison when he announced.
When Trump rolled out his presidential campaign in 2015, the New York Times waited until the 17th paragraph of the story to attack him. But as well known as he is, the paper said at the time, Trump is also widely disliked. Then they cited a pool to back it up. That was the attack on Trump.
Eight years later, the Times attacked Bobby Kennedy in the very first sentence of the story. Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. announced a presidential campaign on Wednesday built on re-litigating COVID-19 shutdowns and shaking Americans faith in science.
Shaking Americans faith in science. Imagine if youre an ordinary New York Times subscriber reading that over your pre-war rent controlled duplex on Columbus Avenue.
Youd think Bobby Kennedy just declared war on the Enlightenment. My fellow Americans, I have come to shake your faith in science. Join me as I drag our nation back to the medieval period. Youd be appalled.
CBS News viewers likely were appalled. In its coverage of Kennedys announcement, CBS denounced the candidates views as misleading and dangerous.
The LA Times called him a thr...
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day
Friday, 23 June
21:18
Drama, Conflict and Challenges Age of Autism The Rebel Alliance!
The Real RFK Jr
biography written by Dick Russell from Skyhorse Publishing debuted
this week on June 20th. This book would be important even if
Robert Kennedy Jr was not running for the Democratic nomination for
the office of President of the United States. However, it's a
non-mainstream media way to learn more about Kennedy.
Click and buy your copies today.
Share with friends, family, Little Free Libraries. We do not
endorse candidates. We will educate, especially where their
campaign overlaps with our topics and mission.
Kennedy has been a stalwart champion for the underdog for
decades. And Lord knows, we're included in the underdog category.
The description sounds a lot like our lives, "An epic biography
filled with drama, conflict, and surmounted challenges."
From the publisher:
The Real RFK Jr. is
an intimate biographical portrait examining the controversial
activist's journey from anguish and addiction to becoming the
country's leading environmental champion fighting government
corruption, corporate greed, and a captured media. Written by his
longtime colleague Dick Russell, the biography also exposes the
misconceptions and explains the rationale behind Kennedy's campaign
to protect public health.
Provided exclusive source material, including access to
Kennedys unpublished writings and personal journals, the author
conducted dozens of interviews with him as well as numerous friends
and associates. Russell delves into everything from Kennedys
sometimes death-defying river rafting adventures to his pioneering
legal cases against polluters such as Smithfield Foods and
Monsanto, while founding the worlds largest water protection group.
The Real RFK Jr. also examines Kennedys pursuit of the truth about
the assassinations of his father and uncle, the wrongful murder
conviction of his cousin, and the false narratives around the
COVID-19 pandemic.
...
21:00
Science-Based Satire: Could Spontaneous Human Combustion Become a Chronic, Treatable Disease? Maybe. Yeah, I think so. Science-Based Medicine
Do humans spontaneously burst into flames? Can these mysterious cases be predicted and kept at bay by homeopathic remedies? No. They don't and they can't. I made it all up. Is it just me, or is getting really hot in here.
The post Science-Based Satire: Could Spontaneous Human Combustion Become a Chronic, Treatable Disease? Maybe. Yeah, I think so. first appeared on Science-Based Medicine.20:00
Plagiarism scandal engulfs high-profile academic in Latvia Retraction Watch
Two years after it was quietly retracted due to plagiarism, a paper by a prominent researcher in Latvia has set the countrys media ablaze, drawing comments from, among others, the minister of education and science and the rector of a leading university.
The plagiarized paper came to public attention in March when the Latvian magazine Ir published serious allegations against Maris Klavins, a professor and former dean at the University of Latvia. The allegations concern possible fraud in an EU-funded project headed by Klavins and include not only plagiarism but data falsification, budget irregularities and suspicious cash payments.
According to Ir, the Latvian police have opened a criminal investigation into the case. Klavins told the magazine he has not been charged in the matter.
In an email to Retraction Watch, Klavins called the allegations lies and said the person responsible for my defamation and persecution was his former PhD student Dmitrijs Porsnovs.
Presently this case is under investigation within a legal process, Klavins added. Considering this, I cannot give comments on the case.
According to the article in Ir, Porsnovs discovered in 2021 that parts of an internal report he had written about the processing of algae for energy production had been published earlier that year by Klavins and others in the journal Agronomy Research without listing him as an author or citing his work. Porsnovs, who is now a graduate student at the University of Stavanger in Norway, did not respond to requests for comments.
The magazine article includes examples of similar text and identical data in Porsnovs report and Klavins paper, titled Algae processing for energy production: development of waste pyrolysis technology. Ir also notes that an e...
13:12
Rosemary extract protects liver mitochondria from oxidative damage and prevents acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 3 ;12(3). Epub 2023 Mar 3. PMID: 36978874 Abstract Title: Rosemary (L.) Glycolic Extract Protects Liver Mitochondria from Oxidative Damage and Prevents Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Abstract: L. (rosemary) is an aromatic culinary herb. Native to the Mediterranean region, it is currently cultivated worldwide. In addition to its use as a condiment in food preparation and in teas, rosemary has been widely employed in folk medicine and cosmetics. Several beneficial effects have been described for rosemary, including antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Here, we investigated the mechanisms accounting for the antioxidant activity of the glycolic extract of() in isolated rat liver mitochondria (RLM) under oxidative stress conditions. We also investigated its protective effect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in vivo. A crude extract was obtained by fractionated percolation, using propylene glycol as a solvent due to its polarity and cosmeceutical compatibility. The quantification of substances with recognized antioxidant action revealed the presence of phenols and flavonoids. Dereplication studies carried out through LC-MS/MS and GC-MS, supported by The Global Natural Product Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) platform, annotated several phenolic compounds, confirming the previous observation. In accordance,decreased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) elicited by Feor-BOOH and inhibited the lipid peroxidation of mitochondrial membranes in a concentration-dependent manner in RLM. Such an effect was also observed in liposomes as membrane models.also prevented the oxidation of mitochondrial protein thiol groups and reduced glutathione (GSH). In model systems,exhibited a potent scavenger activity toward 2,2'-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals and superoxide anions. It also demonstrated an Fechelating activity. Moreover,did not exhibit cytotoxicity or dissipate the mitochondrial membrane potential () in rat liver fibroblasts (BRL3A cells). To evaluate whether such antioxidant protective activity observed in vitro could also be achieved in vivo, a well-established model of hepatotoxicity induced by acute exposure to acetaminophen (AAP) was used. This model depletes GSH and promotes oxidative-stress-mediated tissue damage. The treatment of rats with 0.05%, administered intraperitoneally for four days, resulted in inhibition of AAP-induced lipid peroxidation of the liver and the prevention of hepatotoxicity, maintaining alanine and aspartate aminotransferase (ALT/AST) levels equal to those of the normal, non-treated rats. Together, these findings highlight the potent antioxidant activity of rosemary, which is able to protect mitochondria from oxidative damage in vitro, and effects such as the antioxidant and h...
13:04
Carnosic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Food Funct. 2023 Apr 24 ;14(8):3849-3862. Epub 2023 Apr 24. PMID: 37013966 Abstract Title: Carnosic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through enhancing the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Abstract: Doxorubicin (DOX) is used extensively in anticancer therapy, but its clinical application is limited due to its cardiotoxicity. Carnosic acid (CA) is a bioactive compound found in rosemary. It has been shown to reduce inflammation and reactive oxygen species. The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential cardioprotective effects of CA in response to DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Here, C57BL/6 mice were administered an intraperitoneal injection of DOX (5 mg kg, ip) once a week for three consecutive weeks and treated with CA (40 mg kg, ig) for a three-week experimental period. Forstudy, neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes were used to validate the protective effects of CA (20M) in response to DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. CA markedly suppressed oxidative stress, apoptosis, and pyroptosis responses in the mouse hearts, eventually improving cardiac function. CA showed its antioxidant effect by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) and its downstream heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1); CA also reduced oxidative stress by lowering the MDA and lipid ROS levels and raising the SOD and GSH-px levels. Additionally, CA treatment significantly increased Bcl-2 and inhibited Bax and Caspase-3 cleavage in DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Moreover, CA suppressed the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) pathway to mitigate pyroptosis, as evidenced by lowered caspase1, interleukin-18, and interleukin-1. Consistently, the transfection of Nrf2-siRNA eliminated the protective effects of CA on cardiomyocytes. Altogether, our findings demonstrated that CA inhibited NLRP3 inflammasomesactivating the Nrf2-related cytoprotective system and protected the heart from oxidative damage, apoptosis, and pyroptosis, implying that the use of CA could be a potential therapeutic strategy in the prevention of DOX-associated myocardiopathy.
12:33
Carnosic acid ameliorates indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 9 ;11(3). Epub 2023 Mar 9. PMID: 36979808 Abstract Title: Carnosic Acid Ameliorates Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulceration in Rats by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Abstract: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and indomethacin (IND) are the most commonly prescribed for inflammation or pain. However, widespread use causes several adverse effects, such as gastric ulcers, upper gastric system bleeding, and erosions. Carnosic acid (CA) is an important natural antioxidant found in rosemary (Rosmarinus essentials) and exhibits a protective effect by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation. This study aimed to investigate the impact of CA on IND-induced gastric ulceration. Wistar male rats received CA (100 mg/kg) or esomeprazole (ESP) (20 mg/kg, standard drug) by oral gavage for 14 days, after that gastric ulceration was induced by oral administration of 100 mg/kg IND. CA pretreatment attenuated both gross morphological lesions and histopathological alterations. CA strongly reduced IND-induced oxidative stress, verified by a decrease in MDA (
12:13
Anti- heliobacter pylori and anti-Inflammatory potential of Salvia officinalis metabolites. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Metabolites. 2023 Jan 16 ;13(1). Epub 2023 Jan 16. PMID: 36677061 Abstract Title: Anti-and Anti-Inflammatory Potential ofMetabolites: In Vitro and In Silico Studies. Abstract: Due to its rising antibiotic resistance and associated inflammations,poses a challenge in modern medicine., a member of the Lamiaceae family, is a promising medicinal herb. In this regard, a phytochemical screening followed by GC-MS and LC-MS was done to evaluate the chemical profile of the total ethanolic extract (TES) and the essential oil, respectively. The anti-and the anti-inflammatory activities were evaluated by a micro-well dilution technique and COX-2 inhibition assay. Potential anti-inhibitors were determined by an in silico study. The results revealed that the main metabolites were flavonoids, sterols, volatile oil, saponins, and carbohydrates. The LC-MS negative ionization mode demonstrated 12 compounds, while GC-MS showed 21 compounds. Carnosic acid (37.66%), epirosmanol (20.65%), carnosol1 (3.3%), and 12--methyl carnosol (6.15%) were predominated, while eucalyptol (50.04%) and camphor (17.75%) were dominant in LC-MS and GC-MS, respectively. TES exhibited the strongest anti-activity (3.9g/mL) asymptotic to clarithromycin (0.43g/mL), followed by the oil (15.63g/mL). Carnosic acid has the best-fitting energy to inhibit(-46.6769 Kcal/mol). TES showed the highest reduction in Cox-2 expression approaching celecoxib with IC= 1.70.27g/mL, followed by the oil with IC= 5.30.62g/mL. Our findings suggest thatmetabolites with anti-inflammatory capabilities could be useful inmanagement. Further in vivo studies are required to evaluate and assess its promising activity.
12:05
ALS-L1023 from Melissa officinalis alleviates liver fibrosis in a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 29 ;13(1). Epub 2022 Dec 29. PMID: 36676050 Abstract Title: ALS-L1023 fromAlleviates Liver Fibrosis in a Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model. Abstract: ALS-L1023 is an ingredient extracted fromL. (Labiatae; lemon balm), which is known as a natural medicine that suppresses angiogenesis. Herein, we aimed to determine whether ALS-L1023 could alleviate liver fibrosis in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) model. C57BL/6 wild-type male mice (age, 6 weeks old) were fed a choline-deficient high-fat diet (CDHFD) for 10 weeks to induce NAFLD. For the next 10 weeks, two groups of mice received the test drug along with CDHFD. Two doses (a low dose, 800 mg/kg/day; and a high dose, 1200 mg/kg/day) of ALS-L1023 were selected and mixed with feed for administration. Obeticholic acid (OCA; 10 mg/kg/day) was used as the positive control. Biochemical analysis revealed that the ALS-L1023 low-dose group had significantly decreased alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase. The area of fibrosis significantly decreased due to the administration of ALS-L1023, and the anti-fibrotic effect of ALS-L1023 was greater than that of OCA. RNA sequencing revealed that the responder group had lower expression of genes related to the hedgehog-signaling pathway than the non-responder group. ALS-L1023 may exert anti-fibrotic effects in the NAFLD model, suggesting that it may provide potential benefits for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
12:02
Antiviral potential of Melissa officinalis L.: A literature review. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Nutr Metab Insights. 2023 ;16:11786388221146683. Epub 2023 Jan 12. PMID: 36655201 Abstract Title: Antiviral Potential of Melissa officinalis L.: A Literature Review. Abstract: The use of synthetic drugs has increased in recent years; however, herbal medicine is yet more trusted among a huge population worldwide; This could be due to minimal side effects, affordable prices, and traditional beliefs. Lemongrass () has been widely used for reducing stress and anxiety, increasing appetite and sleep, reducing pain, healing wounds, and treating poisonous insect bites and bee stings for a long time. Today, research has shown that this plant can also fight viruses including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV), and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) through various mechanisms such as inhibiting HSV-1 from binding to host cell, inhibiting HSV-1 replication during the post-adsorption or inhibiting main protease and spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, furthermore, be effective in treating related diseases. This Review investigated the antiviral properties ofand its effect on viral diseases. More in vitro and in vivo studies are needed to determineunderlying mechanism, and more randomized controlled trials should be done to identify its effect in humans. Also, due to the usefulness and lack of side effects, it can be used more as a complementary medicine.
11:59
Melissa Officinalis L. aqueous extract pretreatment decreases methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Ann Nucl Med. 2023 Mar ;37(3):166-175. Epub 2022 Dec 5. PMID: 36469234 Abstract Title: Melissa Officinalis L. aqueous extract pretreatment decreases methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity at lower dose and increasesTc-phytate liver uptake, as a probe of liver toxicity assessment, in rats. Abstract: OBJECTIVE: Hepatotoxicity remains amongst the restricting factors of Methotrexate (MTX)-associated cancer therapy, especially in high doses of chemo-drugs or prolonged treatment. Due to the known protective effects of Melissa officinalis (M. officinalis), the aqueous extract of this plant was evaluated to ameliorate MTX-associated hepatotoxicity in rats.METHODS: Adult female Wistar rats were received or not M. officinalis aqueous extract at doses of 100 mg/kg (for 14 and 24 consecutive days) and 2 g/kg (for 14 consecutive days) by gavage technique. MTX (20 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected on the 10th- and 20th-day post-M. officinalis treatment. 24 h after the last day of treatment,Tc-phytate was intravenously injected through the tail of rats. Animals were killed at 20 min after radiocolloid injection, and vital tissues including the liver and spleen were isolated, weighed, and their radioactivity was counted. As well,Tc-phytate scintigraphy and histopathology of the liver were performed for higher accuracy.RESULT: A significant increase in liver radioactivity was detected in M. officinalis+MTX receiving groups compared with the MTX rats which were more robust at a dose of 100 mg/kg for 14 days. Also, a significant reduction in liver radioactivity was evident with M. officinalis extract at a dose of 2 g/kg for 14 days in comparison with the control group, this reduction was not significant at the lower dose of 100 mg/kg. Gamma scintigraphy and histopathological examinations confirmed the hepatoprotective effect of M. officinalis vs MTX-induced liver injury in rats.CONCLUSION: In conclusion, we highlighted the liver uptake ofTc-phytate as a valuable method for assessment of liver toxicity and addressed that M. officinalis pretreatment (100 mg/kg for 14 days) ameliorates the MTX-associated hepatotoxicity in rats; however, M. officinalis itself induces liver toxicity at higher doses.
11:57
Cytotoxic effect of the crude alcoholic extract of the fruits of Citrullus colocynthis on human hepatocyte carcinoma. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Arch Razi Inst. 2022 Aug ;77(4):1389-1395. Epub 2022 Aug 31. PMID: 36883161 Abstract Title: Cytotoxic Effect of the Crude Alcoholic Extract of the Fruits ofon Human Hepatocyte Carcinoma (Hep-G2). Abstract: Theis a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the family. Several pharmacological investigations have been performed based on the medicinal application of. The anticancer and antidiabetic activities of fruit and seed extracts ofhave been studied. Newly developed anticancer/antitumor medications appear to have been developed based on the extracted chemicals fromdue to the high contents of cucurbitacins. The present study aimed to identify the cytotoxic effect of the crude alcoholic extract of plants ofon the growth of human hepatocyte carcinoma (Hep-G2). The results of the chemical (preliminary) examination of the extract indicated that the fruits contain most of the secondary metabolites including Flavonoids, Tannins, Sapiens, Resins, Amino acids, Glycosides, Terpenes, Alkaloids, and Flavonoids. The toxicological effect of the crude extract was investigated by using six half dilutions concentrations of 20,10,5,2.5,1.25, and 0.625g/m at three exposure periods of 24,48, and 72 h using MTT testing. The toxicological effect of the extract appeared for all six concentrations in the Hep-G2 cell line. The highest concentration of 20g/ml had the highest percentage inhibition rate with a significant difference (0.01) and reached 93.361.61 after 72 h of exposure. While the lowest concentration of 0.625g/ml was recorded rate of inhibition of 23.362.34 after 24 h of exposure. The findings of the present study concluded that theis one of the most promising medicinal plants which effectively treats cancer through its inhibitory effect and fatal toxicity on cancer cells.
11:53
A natural glucan from black bean inhibits cancer cell proliferation. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Molecules. 2023 Feb 19 ;28(4). Epub 2023 Feb 19. PMID: 36838963 Abstract Title: A Natural Glucan from Black Bean Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation via PI3K-Akt and MAPK Pathway. Abstract: A natural-1,6-glucan named BBWPW was identified from black beans. Cell viability assay showed that BBWPW inhibited the proliferation of different cancer cells, especially HeLa cells. Flow cytometry analysis indicated that BBWPW suppressed the HeLa cell cycle in the G2/M phase. Consistently, RT-PCR experiments displayed that BBWPW significantly impacts the expression of four marker genes related to the G2/M phase, including,,, and. To explore the molecular mechanism of BBWPW to induce cell cycle arrest, a transcriptome-based target inference approach was utilized to predict the potential upstream pathways of BBWPW and it was found that the PI3K-Akt and MAPK signal pathways had the potential to mediate the effects of BBWPW on the cell cycle. Further experimental tests confirmed that BBWPW increased the expression ofandand decreased the expression ofandThese results suggested that BBWPW could regulate the PI3K-Akt and MAPK pathways to induce cell cycle arrest and ultimately inhibit the proliferation of HeLa cells, providing the potential of the black bean glucan to be a natural anticancer drug.
11:49
Apigenin alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in INS-1 -cells. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Biol Pharm Bull. 2023 ;46(4):630-635. PMID: 37005308 Abstract Title: Apigenin Alleviates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in INS-1-Cells. Abstract: The improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus induced by naturally occurring polyphenols, known as flavonoids, has received considerable attention. However, there is a dearth of information regarding the effect of the trihydroxyflavone apigenin on pancreatic-cell function. In the present study, the anti-diabetic effect of apigenin on pancreatic-cell insulin secretion, apoptosis, and the mechanism underlying its anti-diabetic effects, were investigated in the INS-ID-cell line. The results showed that apigenin concentration-dependently facilitated 11.1-mM glucose-induced insulin secretion, which peaked at 30M. Apigenin also concentration-dependently inhibited the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling proteins, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein (CHOP) and cleaved caspase-3, which was elevated by thapsigargin in INS-1D cells, with peak suppression at 30M. This was strongly correlated with the results of flow cytometric analysis of annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and DNA fragmentation analysis. Moreover, the increased expression of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) induced by thapsigargin was remarkably reduced by apigenin in a concentration-dependent manner. These results suggest that apigenin is an attractive candidate with remarkable and potent anti-diabetic effects on-cells, which are mediated by facilitating glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and preventing ER stress-mediated-cell apoptosis, the latter of which may be possibly mediated by reduced expression of CHOP and TXNIP, thereby promoting-cell survival and function.
11:39
The obtained results highlight that flavonoids may be a useful tool in overcoming antibiotic resistance. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Ann Agric Environ Med. 2023 Mar 31 ;30(1):61-64. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36999857 Abstract Title: Antimicrobial synergistic effects of apigenin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, myricetin and luteolin in combination with some antibiotics. Abstract: INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE: Antimicrobial resistance, which is considered one of the most important problems of the 21 st century, brings many problems with it, such as increasing mortality rates and treatment costs. Difficulties in the treatment of infections caused by resistant microorganisms have led to the search and need for new antimicrobials or new molecules that interact synergistically with antimicrobials. The aim of this study is to investigate whether various flavonoids have synergistic effects with some antibiotics.MATERIAL AND METHODS: During this study, standard bacterial strainsATCC 25922,ATCC 700603,ATCC 9027,ATCC 29213 andATCC 43300 were used. Minimal inhibitory concentrations of all antibiotics and flavonoids were found by the broth microdilution method. Interactions between antibiotics and flavonoids were then determined by using the checkerboard method. Interactions between antibiotics and flavonoids were evaluated according to the FIC index (FIC) results.RESULTS: According to the results of the microdilution test, the bacterial strains used in this study (except for MRSA) were generally sensitive to antibiotics. Interaction study results showed promising results regarding the synergistic interactions of antibiotics with flavonoids. Epigallocatechin gallate and luteolin especially showed synergistic interaction with antibiotics in many microorganisms. It was found that myricetin showed synergistic interaction only with levofloxacin. Likewise, it was detected that apigenin had limited synergistic interaction with antibiotics.CONCLUSIONS: The obtained results highlight that flavonoids may be a useful tool in overcoming antibiotic resistance.
11:19
Kaempferol ameliorates pulmonary vascular remodeling in chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023 May 1 ;466:116478. Epub 2023 Mar 20. PMID: 36940862 Abstract Title: Kaempferol ameliorates pulmonary vascular remodeling in chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension rats via regulating Akt-GSK3-cyclin axis. Abstract: Excessive proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) is considered a major contributor to elevated pulmonary vascular resistance and a key mechanism of vascular remodeling in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (HPH). Kaempferol is a natural flavonoid compound and can be derived from numerous common medicinal herbs and vegetables, which exhibit antiproliferative and proapoptotic properties, however, the effects of kaempferol on vascular remodeling in HPH remain unexplored. In this study, SD rats were placed in a hypobaric hypoxia chamber for four weeks to establish a pulmonary hypertension model and given either kaempferol or sildenafil (an inhibitor of PDE-5) during days 1-28, after which the hemodynamic parameter and pulmonary vascular morphometry were assessed. Furthermore, primary rat PASMCs were exposed to hypoxic conditions to generate a cell proliferation model, then incubated with either kaempferol or LY294002 (an inhibitor of PI3K). Immunoblotting and real-time quantitative PCR assessed the protein and mRNA expression levels in HPH rat lungs and PASMCs. We found that kaempferol reduced pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary vascular remodeling, and alleviated right ventricular hypertrophy in HPH rats. The mechanistic analysis demonstrated that kaempferol reduced the protein levels of phosphorylation of Akt and GSK3, leading to decreased expression of pro-proliferation (CDK2, CDK4, Cyclin D1, and PCNA) and anti-apoptotic related proteins (Bcl-2) and increased expression of pro-apoptosis proteins (Bax and cleaved caspase 3). These results collectively demonstrate that kaempferol ameliorates HPH in rats by inhibiting PASMC proliferation and pro-apoptosis via modulation of the Akt/GSK3/CyclinD axis.
11:15
Quercetin modulates signal transductions and targets non-coding RNAs against cancer development. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Cell Signal. 2023 Jul ;107:110667. Epub 2023 Apr 5. PMID: 37023996 Abstract Title: Quercetin modulates signal transductions and targets non-coding RNAs against cancer development. Abstract: In recent decades, various investigations have indicated that natural compounds have great potential in the prevention and treatment of different chronic disorders including different types of cancer. As a bioactive flavonoid, Quercetin (Qu) is a dietary ingredient enjoying high pharmacological values and health-promoting effects due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characterization. Conclusive in vitro and in vivo evidence has revealed that Qu has great potential in cancer prevention and development. Qu exerts its anticancer influences by altering various cellular processes such as apoptosis, autophagy, angiogenesis, metastasis, cell cycle, and proliferation. In this way, Qu by targeting numerous signaling pathways as well as non-coding RNAs regulates several cellular mechanisms to suppress cancer occurrence and promotion. This review aimed to summarize the impact of Qu on the molecular pathways and non-coding RNAs in modulating various cancer-associated cellular mechanisms.
11:13
Quercetin downregulates the expression of IL15 in cancer cells through DNA methylation. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Mar ;27(6):2580-2590. PMID: 37013776 Abstract Title: Quercetin downregulates the expression of IL15 in cancer cells through DNA methylation. Abstract: OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to investigate the effect of quercetin on cellular immunity (via IL15 expression) against cancer and to elucidate its regulatory mechanism.MATERIALS AND METHODS: HeLa cells and A549 cells were cultured in vitro and were divided into control (DMSO treated) and experimental groups (treated with different concentrations of quercetin). Transcript levels of IL15 and DNA methyltransferase (DNMTS) were measured using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Genomic DNA was extracted, treated with bisulfite, and the promoter region of IL15 was cloned. Finally, Sanger sequencing was used to detect the degree of promoter methylation.RESULTS: Following quercetin treatment, the expression of IL15 was significantly downregulated in HeLa and A549 cells. The methylation level of IL15 promoter in HeLa cells was about twice that of the control group, and the methylation level of IL15 promoter in A549 cells was about three times that of the control group.CONCLUSIONS: Quercetin inhibits cancer cell proliferation while downregulating IL15 expression, and this regulation is achieved by increasing the methylation of the IL15 promoter.
11:11
Protective effects of querectin against MPP+-induced dopaminergic neurons injury. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Mar 2 ;28(3):42. PMID: 37005755 Abstract Title: Protective Effects of Querectin against MPP-Induced Dopaminergic Neurons Injury via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Abstract: BACKGROUND: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common selective and progressive neurodegenerative disorder of nigrostriatal dopaminergic (DA) neurons. Quercetin is a bioflavonoid with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging and anti-cancer properties. However, the exact mechanism by which quercetin exerts its protective effect on DAergic neurons remains unclear.PURPOSE: To investigate the underlying molecular mechanism of quercetin's protective effect on DA neurons using 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-induced PD ferroptosis model.METHODS: MPP+ was used to induce cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y/primary neurons. Cell viability and apoptosis were assessed by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. The expression levels of ferroptosis-related proteins (NCOA4, SLC7A11, Nrf2, and GPX4) were determined by Western blotting. Malondialdehyde (MDA), iron, and GPX4 levels were assesed using corresponding assay kits. Lipid peroxidation was assessed by C11-BODIPY staining.RESULTS: In the MPP+-induced ferroptosis model of SH-SY5Y cells, the expressions of SLC7A11 and GPX4 were inhibited, and the expression of NCOA4 protein was increased, causing the overproduction of MDA and lipid peroxidation. Quercetin can reduce the above changes caused by MPP+, that is, reduce the protein expression of NCOA4 in SH-SY5Y cells, increase SLC7A11 and GPX4 partially inhibited by MPP+, and reduce MDA overproduction and lipid peroxidation to protect DA neurons. Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 could inhibit quercetin-induced increase of GPX4 and SLC7A11 protein expression, indicating that the protective effect of quercetin was mediated through Nrf2.CONCLUSIONS: The results of this study suggest that quercetin regulates ferroptosis through Nrf2-dependent signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y/primary neurons.
11:07
In vitro and molecular docking analysis of quercetin as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Curr Pharm Des. 2023 ;29(11):883-891. PMID: 37005541 Abstract Title: and Molecular Docking Analysis of Quercetin as an Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant. Abstract: INTRODUCTION: Quercetin (3,3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone) is a dietary flavonoid with good antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.AIMS: The present study aims to determine these effects in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) evoked by lipopolysaccharides (LPS).METHODS: The mRNA expression and protein secretion of inflammatory mediators were evaluated by enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), respectively. Western blotting was utilized for assessing p65-NF-B phosphorylation. Ransod kits evaluated the glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the cell lysates. Ultimately, the molecular docking approach was performed to investigate the biological activity of Quercetin against NF-B pathway proteins and antioxidant enzymes.RESULTS: The findings revealed that quercetin significantly attenuated the expression and secretion of inflammatory mediators and p65-NF-B phosphorylation in LPS-induced PBMCs. Additionally, quercetin dose-dependently improved the activities of SOD and GPx enzymes and decreased LPS-mediated oxidative stress in PBMCs. Moreover, quercetin has a considerable binding affinity to IKb, the core element of the NF-B pathway and the antioxidant enzyme SOD.CONCLUSION: The data show that quercetin plays a vital role in ameliorating inflammation and oxidative stress caused by LPS in PBMCs.
11:02
Quercetin and its nano-formulations for brain tumor therapy. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 16 ;15(3). Epub 2023 Mar 16. PMID: 36986827 Abstract Title: Quercetin and Its Nano-Formulations for Brain Tumor Therapy-Current Developments and Future Perspectives for Paediatric Studies. Abstract: The development of efficient treatments for tumors affecting the central nervous system (CNS) remains an open challenge. Particularly, gliomas are the most malignant and lethal form of brain tumors in adults, causing death in patients just over 6 months after diagnosis without treatment. The current treatment protocol consists of surgery, followed using synthetic drugs and radiation. However, the efficacy of these protocols is associated with side effects, poor prognosis and with a median survival of fewer than two years. Recently, many studies were focused on applying plant-derived products to manage various diseases, including brain cancers. Quercetin is a bioactive compound derived from various fruits and vegetables (asparagus, apples, berries, cherries, onions and red leaf lettuce). Numerous in vivo and in vitro studies highlighted that quercetin through multitargeted molecular mechanisms (apoptosis, necrosis, anti-proliferative activity and suppression of tumor invasion and migration) effectively reduces the progression of tumor cells. This review aims to summarize current developments and recent advances of quercetin's anticancer potential in brain tumors. Since all reported studies demonstrating the anti-cancer potential of quercetin were conducted using adult models, it is suggested to expand further research in the field of paediatrics. This could offer new perspectives on brain cancer treatment for paediatric patients.
10:51
Quercetin and its fermented extract as a potential inhibitor of bisphenol A-exposed HT-29 colon cancer cells' viability. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 15 ;24(6). Epub 2023 Mar 15. PMID: 36982678 Abstract Title: Quercetin and Its Fermented Extract as a Potential Inhibitor of Bisphenol A-Exposed HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells' Viability. Abstract: Bisphenol A (BPA) promotes colon cancer by altering the physiological functions of hormones. Quercetin (Q) can regulate signaling pathways through hormone receptors, inhibiting cancer cells. The antiproliferative effects of Q and its fermented extract (FEQ, obtained by Q gastrointestinal digestion and in vitro colonic fermentation) were analyzed in HT-29 cells exposed to BPA. Polyphenols were quantified in FEQ by HPLC and their antioxidant capacity by DPPH and ORAC. Q and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) were quantified in FEQ. Q and FEQ exhibited antioxidant capacity. Cell viability with Q+BPA and FEQ+BPA was 60% and 50%, respectively; less than 20% of dead cells were associated with the necrosis process (LDH). Treatments with Q and Q+BPA induced cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase, and FEQ and FEQ+BPA in the S phase. Compared with other treatments, Q positively modulatedandgenes. Using a gene microarray of thepathway, Q, Q+BPA, FEQ and FEQ+BPA positively modulated genes involved in apoptosis and cell cycle arrest; bisphenol inhibited the expression of pro-apoptotic and cell cycle repressor genes. In silico analyses demonstrated the binding affinity of Q>BPA>DOPAC molecules for ERand ER. Further studies are needed to understand the role of disruptors in colon cancer.
10:48
Quercetin reprograms immunometabolism of macrophages ameliorated lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative damage. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 14 ;24(6). Epub 2023 Mar 14. PMID: 36982615 Abstract Title: Quercetin Reprograms Immunometabolism of Macrophages via the SIRT1/PGC-1Signaling Pathway to Ameliorate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Oxidative Damage. Abstract: The redox system is closely related to changes in cellular metabolism. Regulating immune cell metabolism and preventing abnormal activation by adding antioxidants may become an effective treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation-related diseases. Quercetin is a naturally sourced flavonoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. However, whether quercetin can inhibit LPS-induced oxidative stress in inflammatory macrophages by affecting immunometabolism has been rarely reported. Therefore, the present study combined cell biology and molecular biology methods to investigate the antioxidant effect and mechanism of quercetin in LPS-induced inflammatory macrophages at the RNA and protein levels. Firstly, quercetin was found to attenuate the effect of LPS on macrophage proliferation and reduce LPS-induced cell proliferation and pseudopodia formation by inhibiting cell differentiation, as measured by cell activity and proliferation. Subsequently, through the detection of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory factors and antioxidant enzyme activity, it was found that quercetin can improve the antioxidant enzyme activity of inflammatory macrophages and inhibit their ROS production and overexpression of inflammatory factors. In addition, the results of mitochondrial morphology and mitochondrial function assays showed that quercetin could upregulate the mitochondrial membrane potential, ATP production and ATP synthase content decrease induced by LPS, and reverse the mitochondrial morphology damage to a certain extent. Finally, Western blotting analysis demonstrated that quercetin significantly upregulated the protein expressions of SIRT1 and PGC-1, that were inhibited by LPS. And the inhibitory effects of quercetin on LPS-induced ROS production in macrophages and the protective effects on mitochondrial morphology and membrane potential were significantly decreased by the addition of SIRT1 inhibitors. These results suggested that quercetin reprograms the mitochondria metabolism of macrophages through the SIRT1/PGC-1signaling pathway, thereby exerting its effect of alleviating LPS-induced oxidative stress damage.
10:40
C. papaya was capable of restoring the altered levels in the hepatic tissues of T2DM rats. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Toxics. 2023 Mar 1 ;11(3). Epub 2023 Mar 1. PMID: 36977005 Abstract Title: Hypoglycemic Potential ofin Liver Is Mediated through IRS-2/PI3K/SREBP-1c/GLUT2 Signaling in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Type-2 Diabetic Male Rats. Abstract: Regardless of socioeconomic or demographic background, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, which affects more than half a billion people worldwide, has been steadily increasing over time. The health, emotional, sociological, and economic well-being of people would suffer if this number is not successfully handled. The liver is one of the key organs accountable for sustaining metabolic balance. Elevated levels of reactive oxygen species inhibit the recruitment and activation of IRS-1, IRS-2, and PI3K-Akt downstream signaling cascade. These signaling mechanisms reduce hepatic glucose absorption and glycogenesis while increasing hepatic glucose output and glycogenolysis. In our work, an analysis of the molecular mechanism ofin mitigating hepatic insulin resistance in vivo and in silico was carried out. The gluconeogenic enzymes, glycolytic enzymes, hepatic glycogen tissue concentration, oxidative stress markers, enzymatic antioxidants, protein expression of IRS-2, PI3K, SREBP-1C, and GLUT-2 were evaluated in the liver tissues of high-fat-diet streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats using q-RT-PCR as well as immunohistochemistry and histopathology. Upon treatment,restored the protein and gene expression in the liver. In the docking analysis, quercetin, kaempferol, caffeic acid, and p-coumaric acid present in the extract were found to have high binding affinities against IRS-2, PI3K, SREBP-1c, and GLUT-2, which may have contributed much to the antidiabetic property of. Thus,was capable of restoring the altered levels in the hepatic tissues of T2DM rats, reversing hepatic insulin resistance.
10:00
Will DARPA Make a Travel Adapter for Human Body? Articles
Another day, another bit of great news, folks. Everyones favorite agency, DARPA, is promising to develop a "travel adapter" for the human body. The travel adapter, intended for "warfighters," is supposed to play a magical trick on biology and program the soldiers sleep cycles at will, as well as disinfect food and water in the soldiers belly in real time. The miracle is going to be a transient and non-genetic "implantable or ingestible bioelectronic carrier."
Certainly, nothing can go wrong, and the proof is this very professionally done image on their website that shows us how one can "program" physiology by adjusting a slider in an app. This image alone is a masterpiece of seduction, selling the appealing-but-totally-fictional concept of getting "something for nothing," as if pulling it out of a magicians hat.
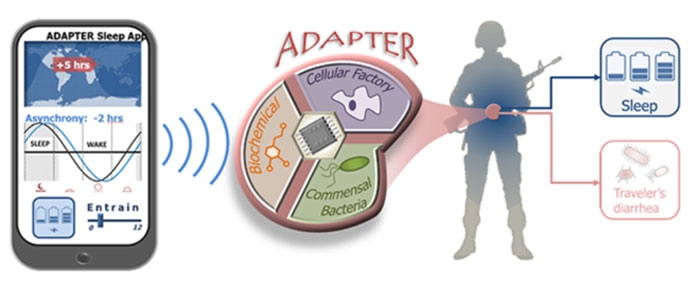
Betraying the Soldiers
Before we get down to the nitty-gritty of DARPAs ADAPTER program yes, the name of the program is acronym but they also call the device an "adapter," DARPA word weavers are crafty like that! I want to express my indignation at the entire vampire-like model of sacrificing human beings to senseless wars.
These wars are fought primarily to make a small crew of shameless people obscenely rich, and the biggest "beneficiaries" of the cruelty dont fight in those wars themselves, just organize the dark business of shedding other peoples blood.
Such betrayal! A lot of people on the ground join the military for noble reasons. Yes, some join out of desperation, to lift themselves out of poverty but many join for very sacred reasons, out of courage, to protect their own.
And then those brave young people get dragged into treacherous carnage, maimed in body and spirit, and sometimes experimented on (here is one pre-2020 example of the U.S. military experimenting on its soldiers, here is another, and we know what happened with COVID "vaccines").
Bioweapon Experimentation on Soldiers
Here is a phenomenally frank 2015 paper titled, "Science wars How much risk should soldiers be exposed to in military experimentation?"
The paper argues that because the warfare is shifting toward the use of bioweapons, it is appropriate to experiment on soldiers as they have already agreed to risk their lives for the benefit of the state:
"With the threat of biological war becoming a more and more dis...
The Benefits of Curcumin in Tumor Treatments Articles
Editor's Note: This article is a reprint. It was originally published March 2, 2014.
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death. What if there were a safe, natural herb that could work for nearly every type of cancer?
According to Dr. William LaValley, who focuses most of his clinical work on the treatment of cancer, curcumin a derivative of turmeric and the pigment that gives the curry spice turmeric its yellow-orange color may fit the bill. It's a natural compound that has been extensively researched, and has been found to have numerous health applications.
Like me, LaValley was trained in general medicine, but he's devoted a considerable amount of time to understanding the biochemical pathways that can support health nutritionally. In 1982, he participated in an exchange program to the People's Republic of China, where he got first-hand experience with the ancient practices of traditional Chinese medicine and acupuncture.
"One of the important messages that I learned there was that natural products, natural molecules, from plants and animals that are already available in nature, have been used by the Chinese for at least hundreds, probably thousands of years. That deeply changed my perspective in the world of medicine," he says.
"I came back to medical school, and thereafter, looked at how I could integrate the perspective of conventional pharmaceutical administration as well as natural extract, natural product administration."
Curcumin Has Potent Anticancer Activity
In 2005, he took a 75% sabbatical from clinical practice to immerse himself in the science of molecular biology, specifically the molecular biology of cancer. He also devoted approximately 9,000 to 9,500 hours building a relational database from the PubMed literature about the molecular biology of cancer.
One important lesson he learned through that venture is that the understanding of molecular biology can be applied across a range of diseases and symptoms described in the scientific literature. That knowledge can be applied by searching PubMed and other related databases, looking at the relevant molecular pathways involved.
..."In learning the molecular biology of cancer pathways, and in learning that what the evidence actually shows for the effect of natural product extracts on various relevant molecular targets in various cancers, we see that there's actually quite a large amount of evidence that supports using various molecules, natural products, and pharmaceuticals that are already approved and that have been around for a long time to affect anti-cancer activity along that pathway at that target.
Collagen and Gelatin Are Crucial for Optimal Health Articles
Collagen accounts for about 30% of the total protein in your body. One of its primary purposes is to provide structural support and strength to your tissues, such as skin, bones, tendons, ligaments and cartilage1,2,3 by allowing them to stretch while still maintaining tissue integrity.
As such, collagen is crucial for repairing soft tissue, muscle and connective tissue. Connective tissues include tendons, ligaments, cartilage and fascia, which tend to get weaker and less elastic with age. Connective tissue injuries are also problematic since theres very little blood supply in connective tissue, which slows down recovery.
Nearly one-third of the amino acids in collagen is glycine. It is also high in proline, hydroxyproline and alanine, which are the building blocks for the matrix of connective tissue. Your body uses the amino acids in collagen to rehab stressed areas and places in your body where its needed the most. Other lesser-known health benefits of collagen supplementation include:
|
Deeper sleep due to its glycine content4 |
|
Reduced joint pain and stiffness,5 including osteoarthritis pain6 |
|
Improved gut health and digestion, thanks to the presence of glycine7 |
|
Improved blood pressure and reduced cardiovascular damage8 |
|
Improved glucose tolerance9 |
|
Reduced inflammation and oxidative damage, as glycine inhibits the consumption of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). NADPH is used as a reductive reservoir of electrons to recharge antioxidants once they become oxidized |
Important Differences Between Collagen and Red Meat
The chart below details the amino acid ratios of gelatin and collagen versus red meat (beef). As you can see, gelatin/collagen contain vastly more of the important amino acids to rebuild your connective tissue than beef. Since one-third of your bodys protein is collagen, it makes no sense to eat only muscle meat, as it will not provide enough amino acids to allow you to build strong connective t...
09:18
Discovery of potential phytochemicals from Carica papaya targeting BRCA-1 in breast cancer treatment. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 29. Epub 2023 Mar 29. PMID: 36988843 Abstract Title: Discovery of Potential Phytochemicals from Carica papaya Targeting BRCA-1 in Breast Cancer Treatment. Abstract: The BRCA1 and BRCA2 are genes that encode a protein that ensures the integrity of DNA and prevents the unregulated cells from proliferating. Mutations in the sequence of these genes are associated with the birth of inherited breast cancers. The research for possible human breast cancer treatment remains a vital step in the drug development process. In this study, in silico investigations involving a computational method for the discovery of active phytochemicals from Carica papaya against the BRCA-1 gene were carried out. The in silico studies for these phytochemicals datasets as BRCA-1 breast cancer therapeutic agents showed promising results through pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics studies. The Carica papaya compounds were found to follow the rule of five and have good bioavailability. The ADMET and drug-likeness screening score of the identified ligands also recognized their potential as a promising drug candidate against BRCA-1 while the DFT also confirm better biological and chemical reactivity of Carica papaya compounds with excellent intra-molecular charge transfer between electron donor and electron acceptor site. The results of the molecular docking provided useful information on possible target-lead interactions, demonstrating that the newly developed leads showed a high affinity for BRCA-1 targets and might be investigated for further research.
09:09
Cytotoxic activity of the ethyl acetate extract of Iraqi Carica papaya leaves in breast and lung cancer cell lines. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Feb 1 ;24(2):581-586. Epub 2023 Feb 1. PMID: 36853308 Abstract Title: Cytotoxic Activity of the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Iraqi Carica papaya Leaves in Breast and Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Abstract: UNLABELLED: The aim of this study was to evaluate the cytotoxic effect of the ethyl acetate fraction of Iraqi Carica papaya (C. papaya) in breast and lung cancer cell lines, MCF-7 and A549, respectively.METHODS: The ethyl acetate extract of Iraqi C. papaya leaves was prepared and tested for its phytochemical constitution. The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazoline-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was performed in breast (MCF-7) and lung (A549) cells lines that were treated with different concentrations of ethyl acetate extract (3.125,6.25,12.5, 25, 50, and 100g/ml). After 72 hrs of treatment, cell viability was evaluated.RESULTS: The ethyl acetate extract of C. papaya showed considerable cytotoxic activity in the MCF-7 and A549 cell lines. The activity was dose-dependent; The half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were 22.74g/ml and 8.674g/ml in the MCF-7 and A549 cell lines, respectively.CONCLUSION: The ethyl acetate fraction of Iraqi C. papaya leaves has potential anticancer activity in lung and breast cancer.
09:07
DHS Sought to Assign Social Credit Style "Risk Scores" to Social Media Users GreenMedInfo
Newly-obtained documents reveal.
09:04
DHS Sought to Assign Social Credit Style "Risk Scores" to Social Media Users GreenMedInfo

Originally published on www.reclaimthenet.org
by Cindy Harper
In a sharp spotlight on the interplay between national security and individual privacy, newly disclosed documents have unveiled that the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) entered into a contract with the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) in 2018 to develop a project, dubbed "Night Fury," designed to analyze and assign "risk scores" to social media accounts.
08:59
Astragaloside IV alleviates 1-deoxysphinganine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction during the progression of chronic kidney disease. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Front Pharmacol. 2023 ;14:1092475. Epub 2023 Mar 24. PMID: 37033627 Abstract Title: Astragaloside IV alleviates 1-deoxysphinganine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction during the progression of chronic kidney disease through p62-Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Abstract: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) can lead to significant elevation of 1-deoxysphingolipids (1-deoxySL). The increase of 1-deoxySL in turn can result in mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress, which can cause further progression of CKD.This study assessed the therapeutic effect of Astragaloside IV (AST) against 1-deoxySL-induced cytotoxicityand in rats with CKD. HK-2 cells were exposed to 1-deoxysphinganine (doxSA) or doxSA + AST. doxSA-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress were evaluated by immunostaining, real-time PCR, oxidative stress sensor, and transmission electron microscopy. The potential effects of AST on kidney damage were evaluated in a rat 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6 Nx) model of CKD.The findings ofexperiments showed that doxSA induced mitochondrial damage, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. AST markedly reduced the level of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, lowered apoptosis, and improved mitochondrial function. In addition, exposure to AST significantly induced the phosphorylation of p62 and the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 as well as its downstream anti-oxidant genes. p62 knock-down fully abolished Nrf2 nuclear translocation in cells after AST treatment. However, p62 knock-down did not affect TBHQ-induced Nrf2 nuclear translocation, indicating that AST can ameliorate doxSA-induced oxidative stress through modulation of p62 phosphorylation and Nrf2 nuclear translocation.The findings indicate that AST can activate Nrf2 antioxidant pathway in a p62 dependent manner. The anti-oxidative stress effect and the further mitochondrial protective effect of AST represent a promising therapeutic strategy for the progression of CKD.
08:54
Astragaloside IV attenuates podocyte apoptosis through ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Jul ;203:45-57. Epub 2023 Apr 6. PMID: 37030337 Abstract Title: Astragaloside IV attenuates podocyte apoptosis through ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction by up-regulated Nrf2-ARE/TFAM signaling in diabetic kidney disease. Abstract: Defective antioxidant system as well as mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the pathogenesis and progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated signaling is the central defensive mechanism against oxidative stress and therefore pharmacological activation of Nrf2 is a promising therapeutic strategy. In this study, using molecular docking we found that Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), an active ingredient from traditional formula of Huangqi decoction (HQD), exerted a higher potential to promote Nrf2 escape from Keap1-Nrf2 interaction via competitively bind to amino acid sites in Keap1. When podocyte exposed to high glucose (HG) stimulation, mitochondrial morphological alterations and podocyte apoptosis were presented and accompanied by Nrf2 and mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) downregulation. Mechanistically, HG promoted a decrease in mitochondria-specific electron transport chain (ETC) complexes, ATP synthesis and mtDNA content as well as increased ROS production. Conversely, all these mitochondrial defects were dramatically alleviated by AS-IV, but suppression of Nrf2 with inhibitor or siRNA and TFAM siRNA simultaneously alleviated the AS-IV efficacy. Moreover, experimental diabetic mice exhibited significant renal injury as well as mitochondrial disorder, corresponding with the decreased expression of Nrf2 and TFAM. On the contrary, AS-IV reversed the abnormality and the Nrf2 and TFAM expression were also restored. Taken together, the present findings demonstrate the improvement of AS-IV on mitochondrial function, thereby resistance to oxidative stress-induced diabetic kidney injury and podocyte apoptosis, and the process is closely associated with activation of Nrf2-ARE/TFAM signaling.
08:46
Astragaloside IV targets PRDX6, inhibits the activation of RAC subunit in NADPH oxidase 2 for oxidative damage. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Phytomedicine. 2023 Jun ;114:154795. Epub 2023 Mar 29. PMID: 37030053 Abstract Title: Astragaloside IV targets PRDX6, inhibits the activation of RAC subunit in NADPH oxidase 2 for oxidative damage. Abstract: BACKGROUND: Radix Astragali Mongolici, as a traditional Chinese medicine, is widely used in the treatment of qi deficiency, viral or bacterial infection, inflammation and cancer. Astragaloside IV (AST), a key active compound in Radix Astragali Mongolici, has been shown to reduce disease progression by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. However, the specific target and mechanism of action of AST in improving oxidative stress are still unclear.PURPOSE: This study aims to explore the target and mechanism of AST to improve oxidative stress, and to explain the biological process of oxidative stress.METHODS: AST functional probes were designed to capture target proteins and combined with protein spectrum to analyze target proteins. Small molecule and protein interaction technologies were used to verify the mode of action, while computer dynamics simulation technology was used to analyze the site of interaction with the target protein. The pharmacological activity of AST in improving oxidative stress was evaluated in a mouse model of acute lung injury induced by LPS. Additionally, pharmacological and serial molecular biological approaches were used to explore the underlying mechanism of action.RESULTS: AST inhibits PLA2 activity in PRDX6 by targeting the PLA2 catalytic triad pocket. This binding alters the conformation and structural stability of PRDX6 and interferes with the interaction between PRDX6 and RAC, hindering the activation of the RAC-GDI heterodimer. Inactivation of RAC prevents NOX2 maturation, attenuates superoxide anion production, and improves oxidative stress damage.CONCLUSION: The findings of this research indicate that AST impedes PLA2 activity by acting on the catalytic triad of PRDX6. This, in turn, disrupts the interaction between PRDX6 and RAC, thereby hindering the maturation of NOX2 and diminishing the oxidative stress damage.
08:33
Astragaloside IV alleviates stroke-triggered early brain injury. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Acta Cir Bras. 2023 ;38:e380723. Epub 2023 Mar 24. PMID: 36995819 Abstract Title: Astragaloside IV alleviates stroke-triggered early brain injury by modulating neuroinflammation and ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Abstract: PURPOSE: Stroke is an acute cerebrovascular disease. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is an active ingredient extracted from Astragalus membranaceus with an established therapeutic effect on central nervous system diseases. This study examined the neuroprotective properties and possible mechanisms of AS-IV in stroke-triggered early brain injury (EBI) in a rat transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model.METHODS: The neurological scores and brain water content were analyzed. 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining was utilized to determine the infarct volume, neuroinflammatory cytokine levels, and ferroptosis-related genes and proteins, and neuronal damage and molecular mechanisms were evaluated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dutp nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining, western blotting, and real-time polymerase chain reaction.RESULTS: AS-IV administration decreased the infarct volume, brain edema, neurological deficits, and inflammatory cytokines TNF-, interleukin-1(IL-1), IL-6, and NF-B, increased the levels of SLC7A11 and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), decreased lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and prevented neuronal ferroptosis. Meanwhile, AS-IV triggered the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and alleviated ferroptosis due to the induction of stroke.CONCLUSIONS: Hence, the findings of this research illustrate that AS-IV administration can improve delayed ischemic neurological deficits and decrease neuronal death by modulating nuroinflammation and ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
08:25
Astragaloside IV induces the protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Mar 27:1-18. Epub 2023 Mar 27. PMID: 36971224 Abstract Title: Astragaloside IV induces the protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction by inducing angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis. Abstract: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMECs)-derived exosomes (MSC-Exo) can improve acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) has also been reported to have cardioprotective pharmacological effects. However, it is not entirely clear whether AS-IV can improve AMI by inducing MSC-Exo. BMSCs and MSC-Exo were isolated and identified, and we also established the AMI rat model and the OGD/R model with H9c2 cells. After MSC-Exo or AS-IV-mediated MSC-Exo treatment, cell angiogenesis, migration, and apoptosis were evaluated by tube formation, wound healing, and TUNEL staining. The cardiac function of the rats was measured by echocardiography. The pathological changes and collagen deposition in rats were also assessed with Masson and Sirius red staining. The levels of-SMA, CD31 and inflammatory factors were determined by immunohistochemistry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)., AS-IV-mediated MSC-Exo can significantly enhance the angiogenesis and migration of H9c2 cells induced by OGD/R, and significantly reduce their apoptosis., AS-IV-mediated MSC-Exo can improve the cardiac function of rats, and attenuate pathological damage and collagen deposition in AMI model rats. In addition, AS-IV-mediated MSC-Exo can also promote angiogenesis and reduce inflammatory factors in rats with AMI. AS-IV-stimulated MSC-Exo can improve myocardial contractile function, myocardial fibrosis and angiogenesis, reduce inflammatory factors and induce apoptosis in rats after AMI.
08:11
Palmitoylethanolamide in the treatment of chronic pain. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Nutrients. 2023 Mar 10 ;15(6). Epub 2023 Mar 10. PMID: 36986081 Abstract Title: Palmitoylethanolamide in the Treatment of Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials. Abstract: Chronic pain is a major source of morbidity for which there are limited effective treatments. Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), a naturally occurring fatty acid amide, has demonstrated utility in the treatment of neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Emerging reports have supported a possible role for its use in the treatment of chronic pain, although this remains controversial. We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis to examine the efficacy of PEA as an analgesic agent for chronic pain. A systematic literature search was performed, using the databases MEDLINE and Web of Science, to identify double-blind randomized controlled trials comparing PEA to placebo or active comparators in the treatment of chronic pain. All articles were independently screened by two reviewers. The primary outcome was pain intensity scores, for which a meta-analysis was undertaken using a random effects statistical model. Secondary outcomes including quality of life, functional status, and side effects are represented in a narrative synthesis. Our literature search identified 253 unique articles, of which 11 were ultimately included in the narrative synthesis and meta-analysis. Collectively, these articles described a combined sample size of 774 patients. PEA was found to reduce pain scores relative to comparators in a pooled estimate, with a standard mean difference of 1.68 (95% CI 1.05 to 2.31,= 0.00001). Several studies reported additional benefits of PEA for quality of life and functional status, and no major side effects were attributed to PEA in any study. The results of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that PEA is an effective and well-tolerated treatment for chronic pain. Further study is warranted to determine the optimal dosing and administration parameters of PEA for analgesic effects in the context of chronic pain.
08:00
Happy Hour Series with Lee Kessler: The White King Pt 4 Dr. Tenpenny
06-22-2023 Audio Version here: If you prefer to watch rather than listen, click on the video below: https://drtenpenny.b-cdn.net/2023/06-22-23-HHr-LeeKessler-Pt4.mp4 The White King book series are modern day allegories told through []
07:42
An Introduction to the Trieste Model of Mental Health Care, and Why It Matters Mad In America
From Vincenzo Passante/Psychiatry at the Margins: This approach is the basis (at least on paper) of the entire mental health system in Italy. So what is the Trieste model exactly?
. . . Anyone who is interested in the Trieste model should [get] to know its history, what the Basaglians always stood against in traditional psychiatry but also how they differed from other movements critical of psychiatry in the way they envisioned change.
While the Basaglian approach had significant influence outside Italy (for example in South America), it has been almost completely ignored in the US, and the UK has arguably been the most resistant country in the world to Basaglian practice since the 80s, with the beginning of a change of heart becoming evident only in very recent years. As a Basaglian who is originally from Trieste and now lives in the UK, I therefore face an up-hill task in influencing the English-speaking world on this subject.
. . . The system in Trieste is organized around a number of community mental health centers, the number of which varied across the years. Aside from a brief period for one of them currently, they are normally all open 24/7. These settings include beds for people who need them, but are also places where people can meet to pass some time with others, see a psychologist or another professional. They are therefore both crisis and not-crisis services, in line with the idea that freedom is therapeutic, which was one of the mottos of the revolution.
There is also a general hospital ward (the last time I visited, in April this year, it had 7 beds and 5 were occupied, but before the local government started cutting services, this place was often almost empty). There are no locked doors and no restraint is used across the whole mental health system. Conflict is resolved by means of negotiation and compromise. Help is not structured around treatment pathways based on a diagnosis (or alternative fixed conceptualizations), but on the persons whole life and needs across the board. This does not mean that disorders are not believed to exist, nor that technical interventions are not used, but that we put the illness in brackets and that we operate way beyond treatment. It means that intra-psychic problems exist within a whole life and societal context and that the context in itself can be part of both the problem and of the solution. The approach is to suspend judgement on the exact nature of a persons problem at the beginning of the relationship, and gradually help the person make sense of their life within a dialectical context.
These are the basic facts about the system and the vision of care that underpins it. The reaction from UK professionals to this picture is sometimes enthusiasm, sometimes curiosity and sometimes skepticism.
To address questions and concerns, I would like to briefly address a number of common objections I enc...
06:30
Empath Personalities Suffer From Overwhelming Emotional & Spiritual Exhaustion; Heres What It Looks Like And How To Shield Healthy Holistic Living
The term empathy finds its roots in two Greek words: em meaning in, and pathos meaning feeling. It denotes the capacity to understand and share the feelings of others. When it comes to individuals, empathic people demonstrate this emotional sensitivity at a higher level, often sensing the emotions and energies of those around them more intensely. Here are several traits that can help define an empathic person.

High Sensitivity
Empaths are typically more sensitive than the average person. They are deeply in tune with their own emotions and the emotions of others, often absorbing feelings from people around them. This heightened sensitivity can extend beyond emotions, including sensitivity to noise, smells, and large crowds.
Intuition
Empaths often exhibit strong intuitive abilities. They can sense the mood of a room when they walk in or intuit what someone is feeling without explicit communication. This allows them to understand others deeply, but it can also be draining if not managed effectively.
Emotional Absorption
Perhaps one of the most distinct characteristics of empaths is their tendency to absorb the emotions of others. They can often feel others pain, joy, and other emotions as if they were their own. This can make them excellent friends and partners as they genuinely understand and sympathize with the feelings of others.
Giving Nature
Empaths are naturally giving and nurturing. They tend to put others needs before their own and are driven by a desire to alleviate others suffering or enhance their happiness. This makes them great caregivers and healers, but it can also lead to feelings of exhaustion if they neglect their own...
06:26
Do physicians study vaccines? Absolutely, sorry anti-vaxxers Skeptical Raptor
The Skeptical Raptor, stalking pseudoscience in the internet jungle.
Anti-vaxxers love to state that physicians dont study vaccines. Of course, those same anti-vaxxers employ their Dunning-Kruger cognitive bias to claim that their 30 minutes of Google University research makes them the only experts in the world about vaccines. Using that logic, I could become an authorized Ferrari mechanic after watching a 30-minute YouTube video Read More Do physicians study vaccines? Absolutely, sorry anti-vaxxers
05:59
18 Anti-Parasitic Foods and Herbs To Add To Your Diet Healthy Holistic Living
Parasites are organisms that depend on a host for their survival. They attach themselves to or invade another living organism, feeding off their hosts nutrients and often causing health problems in the process. The host may experience a spectrum of health issues from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to debilitating diseases. These unwelcome guests can infiltrate your body in a variety of ways: consuming contaminated food or water, bites from insects, sexual contact, or even simply walking barefoot on contaminated soil.
However, the good news is that a careful choice of dietary intake can serve as a natural defense mechanism against such parasitic infections. This article aims to provide you with a detailed understanding of the best anti-parasitic foods, their health benefits, the scientific studies backing their use, and additional tips on how to incorporate them into your daily diet.
So how do you know if you have parasites? There are countless kinds of parasites that exist and many of them are so common, that you may even be unaware that some of the problems youre experiencing could be because of parasites.

Top 10 Signs You May Have A Parasite:
- Unexplained constipation, diarrhea, gas, or IBS symptoms
- Youve had travelers diarrhea while traveling internationally
- You have a history of food poisoning and are still dealing with digestive issues
- You have...
05:45
Basic vaccine chemistry for anti-vaxxers Skeptical Raptor
The Skeptical Raptor, stalking pseudoscience in the internet jungle.
One of the problems, among many, with anti-vaccine activists, is a complete misunderstanding of the basics of vaccine chemistry. People get scared of long chemical names, or chemicals themselves, and wonder if a vaccine might be dangerous. Setting aside the fact that vaccines undergo substantial and robust preclinical and clinical testing which has shown that Read More Basic vaccine chemistry for anti-vaxxers
04:27
Hone In On Healthy Blood Sugar Levels Dr. Tenpenny
One of the most frequent things we tell our patients at my clinics regards the importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Keeping blood sugar within the target range can []
03:00
Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics at the Crossroads: Mary Boyle Interviews Jay Joseph Mad In America
In 2004 I was interviewed by Craig Newnes for The Psychologist, a journal published by the British Psychological Society. The occasion was the publication of my first book, The Gene Illusion: Genetic Research in Psychiatry and Psychology Under the Microscope. Upon publishing my fourth book, Schizophrenia and Genetics: The End of An Illusion (2023), psychologist/author Mary Boyle invited me for a new interview to discuss the book and the changes that have occurred in behavioral science genetic research since 2004. Marys questions, and my answers, are found below. Jay Joseph

Mary Boyle: Jay, you were interviewed in 2004 about your book The Gene Illusion. It was a detailed critique of genetic research on schizophrenia, IQ and criminality and you concluded that there was little if any scientifically valid evidence in support of genetic influences on human behavioral differences. Your latest book, Schizophrenia and Genetics: The End of An Illusion has just been published. It, and your many other publications, show that a lot has happened in psychiatric and behavioral genetics research over the last 20 years. Well be talking about what has and hasnt changed and whether your earlier conclusion still stands. But first, tell us how you became interested in this area and what keeps you engaged with it.
Jay Joseph: I became interested in the genetics of schizophrenia topic as a U.S. clinical psychology graduate student in the mid-1990s. The arguments fascinated me, and because I saw the genetic argument as weak, it was stunning to hear that the debate had been largely closed in favor of genetics by the 1980s. My desire to learn more about genetic research led me...
02:00
EPA Breaking the Law to Help Pesticide Companies Alliance for Natural Health USA Protecting Natural Health
The agency is giving pesticide-coated seeds a pass as they poison local communities and destroy ecosystems. Action Alert!
Over the last few months, weve been reporting on the health and environmental catastrophe linked to the use of pesticide-coated seeds, which were utilized to produce ethanol at a plant in Mead, Nebraska.
Incredibly, the use of pesticide-coated seeds, both in ethanol production and to grow food, is completely legal, and the EPA has refused to regulate these toxic seeds, probably because it does not want to step on the toes of big agribusinesses. The agency is now being sued by advocacy groups for violating its own pesticide laws. Think about this: the agency charged with protecting the environment and human health needs to be challenged in court to protect the environment and human health over industry profits. It is a sad commentary on state of affairs in Washington, but we must help hold the agencys feet to the fire.
The lawsuit, brought forth by the Center for Food Safety and the Pesticide Action Network, seeks to close a loophole at the EPA that allows seeds coated with neonicotinoid (neonic for short) pesticides to evade regulation under federal pesticide laws. The groups argue that pesticide-coated seeds should be regulated like other pesticides under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), which would trigger closer regulatory scrutiny, in particular an analysis of the seeds benefits versus their costs to the environment and human health. Notably, if neonic-coated seeds were regulated under FIFRA, the EPA would have to show that the seeds do not cause unreasonable or adverse effects to the environment. As we will discuss below, this would be a heavy lift for the EPA, which is likely the reason the agency is fighting to keep the loophole open.
The EPA claims that the seeds fall under an exemption to FIFRA called the Treated Article Exception. These are items treated with pesticides to protect the item itself. The...
01:53
ANHs Free Speech Fight Gains Momentum Alliance for Natural Health USA Protecting Natural Health
ANH-USAs efforts to get to the bottom of the Federal Trade Commissions (FTC) latest free speech attack is picking up steam and getting important coverage in the media. Action Alert!
Last week, we reported that we submitted a Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request to learn the real motivations for the FTCs attack on free speech in the natural products sector. Our FOIA request stems from concerns that the FTCs recent guidance will have the effect of limiting consumer access to vital scientific information about the benefits of dietary supplements and other natural products. We believe the agency is poised to start cracking down on health claims related to nutrients, and we want to learn how the new FTC policy was generated, which could potentially serve as the basis for a legal challenge to the agencys overreach.
Independent news outlets have taken notice of our efforts. You can see coverage of our important work in this area here, here, and here.
Were facing a government-led campaign to conceal the remarkable truth about the healing and disease-preventing powers of foods and nutrients, ultimately misleading the public so that they spend their money on drugs rather than natural supplements.
Lets keep up the momentum. Help us push back against the governments censorship campaign and support free speech!
Action Alert! Write to Congress and the FTC, telling them to complete ANHs FOIA request. Please send your message immediately.
The post ANHs Free Speech Fight Gains Momentum first appeared on Alliance for Natural Health USA - Protecting Natural Health.
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day
Thursday, 22 June
23:20
How I Requeened My Beehive The Healthy Home Economist
How to requeen a beehive when the existing queen dies or becomes unproductive to maintain the viability of the colony. Many of you know via my social media channels that I received a beehive and beekeeper training lessons as a Christmas present last year. Here is the website of my awesome and incredibly knowledgeable beekeeper,
The post How I Requeened My Beehive appeared first on The Healthy Home Economist.
23:00
Can Kinesiology Tape Increase Oxygen Delivery and Improve Sports Performance? Science-Based Medicine
USA Track & Field is endorsing a kinesiology tape that is claimed to improve cell oxygenation.
The post Can Kinesiology Tape Increase Oxygen Delivery and Improve Sports Performance? first appeared on Science-Based Medicine.20:00
Financial advisor failed to disclose he had sued the organization his paper criticized Retraction Watch
Earlier this year, a financial advisor published a paper purporting to find that his colleagues who had pursued accreditation as Certified Financial Planners (CFPs) were more likely to engage in misconduct.
What the paper didnt mention: That he had sued the CFP Board, the organization that offered that certification, and given up his own CFP marks over a dispute regarding the integrity of the CFP Boards disciplinary process, according to a correction to the article published in April.
The editors have determined its disclosure would not have impacted the peer review process, but it has since been added to the article for the benefit of readers, the notice stated.
The article, Badges of Misconduct: Consumer Rules to Avoid Abusive Financial Advisers, was published in the Journal of Financial Regulation in February. In the abstract, the authors described their findings:
Using an adviser misconduct scoring framework we report specific misconduct ratings for each of the 625,980 Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) advisers, finding elevated misconduct for Certified Financial Planner (CFP) professionals and commission/fiduciary licensees.
The authors concluded that their findings suggest that consumers who rely on a single market signal should avoid CFP professionals if they wish to reduce misconduct risk. But one of the groups former collaborators has raised concerns that aspects of the methodology make the findings unreliable.
The papers first author and the subject of the correction notice, Jeffrey Camarda, a financial advisor with his own firm in Jacksonville, Fla., told Retraction Watch that my CFP disciplinary issues are pretty...
12:39
Algonac City Council approves planning commission reappointments. Water plant items also discussed Fluoride Action Network
Algonac City Council members approved reappointments to the planning commission and discussed several water plant items at a June 20 meeting.
Mayor Rocky Gillis said four planning commission board members had terms expiring July 17 and would like to be considered for reappointment: Rich Arpan, Amanda Hass, Brian Tideswell and Mark Thompson.
The boards and commissions appointment policy approved by city council in December 2015 states that no new applicants would be sought out in the case of a requested reappointment, unless by majority of the council, Gillis said.
Council member Corey Blair made a motion to approve the reappointments of Arpan, Hass, Tideswell and Thompson to the planning commission for three-year terms ending July 1, 2026.
He thanked each of them.
Their reappointment makes everything a lot smoother, especially with everybody still within the group and been on the group for a while, so I commend them and say thank you, he said.
Theyre all good people, council member Michael Bembas said.
Gillis agreed, and the motion was unanimously approved.
Council members also thanked and congratulated those reappointed to the planning commission during the council comment portion of the meeting.
It takes a lot to volunteer for commissions, especially one as important as the planning commission, council member Dawn Davey said.
Mayor Pro Tem Raymond Martin commented that the four are volunteers and give up their time to serve on the commission.
I would also to thank our reappointments, Gillis said. It makes our job much easier and we dont have to go out and search for candidates, so we appreciate their service.
Water Plant Items
The council also discussed several water plant items.
Were being asked to approve water plant fluoride probe replacement, Gillis said. The water plant is required to test the amount of fluoride in both raw water and drinking water. The current probe is no longer working.
He said the city received a quote from USA Blue Book for a new fluoride probe and associated solutions.
Davey made a motion to approve water plant fluoride probe replacement from USA Blue Book in the amount of $1,118.14.
City Manager Denice Gerstenberg said a new fluoride probe was ordered as soon as it was discovered that the previous one was not working anymore.
Bembas suggested ordering a second probe so that if one stops working, there is a backup.
I would like to ask the public services superintendent if that would be beneficial for him and then get back with you, Gerstenberg said.
The motion was unanimously approved.
The council also unanimously approved a motion to approve a one-year maintenance contract for 24-hour monitoring of chlorine levels to Hach in the amount of $4,323.
The water plant has three CL-17 online chlorine analyzers and one bencht...
11:34
Acetaminophen changes Mu rhythm power related to pain empathy. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Neuropsychologia. 2023 Jun 6 ;184:108544. Epub 2023 Mar 21. PMID: 36948452 Abstract Title: Acetaminophen changes Mu rhythm power related to pain empathy. Abstract: Empathy is an intricate ability that entails the subjective feeling and understanding of emotions someone else may be experiencing. Acetaminophen, the active ingredient found in Tylenol, is among the most common pain medications consumed. There is new evidence, however, that suggests this common analgesic may also dampen empathic processes. However, no previous study has investigated the effect acetaminophen may have on pain empathy or mu power during a pain empathy task. Therefore, participants were randomly assigned to either an experimental (acetaminophen) or control (sugar) group in a double-blinded experimental research design aimed to measure mu power, using EEG, and behavioral responses to painful and non-painful images. Participants in the experimental group were administered 1000 mg of acetaminophen, and it was verified that participants were unaware of their group assignment. We found that mu suppression was greater in the acetaminophen group, which was strongest at electrode C3. Additionally, mu power differences between painful and non-painful images were related to trait empathy, and mu power during the painful images were positively correlated with empathy scores. Results from this study suggest that in addition to reducing physical pain, acetaminophen may also change the neural response when perceiving others in pain. The implications of these findings could possibly lead to changes in how we prescribe and administer this common drug.
11:31
Thymol had a unique effect on reducing bone marrow and liver cell-tissue changes due to the acetaminophen toxicity. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023 ;2023:1714884. Epub 2023 Apr 4. PMID: 37056637 Abstract Title: Comparative Effect of the Active Substance of Thyme with N-Acetyl Cysteine on Hematological Parameters and Histopathological Changes of Bone Marrow and Liver in Rat Models of Acetaminophen Toxicity. Abstract: Acetaminophen has always been at the center of attention as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, which is generally associated with the serious side effects on liver and the hematological parameters. This study aimed to compare the effect of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and thyme extract on rat models of acetaminophen-induced toxicity. The present experimental study was conducted on 48 Wistar rats randomized into six groups, including the control group (no treatment); the Ac group (470 mg/kg of acetaminophen); the Ac+100Ex, Ac+200Ex, and Ac+400Ex groups (acetaminophen+thyme extract at doses of 100, 200, 400mg/kg); and Ac+NA group (acetaminophen+NAC). After weighing, a blood sample was taken from heart at the end of the period. The measured parameters were hematological, liver biochemical, and oxidative stress profiles. A part of the liver tissue was also fixed for the pathological examinations. The bone marrow was aspirated to check for cellular changes as well. The lowest mean of the final weight and liver weight to body weight ratio was observed in the Ac group. Weight loss was compensated in Ac+NA and Ac+200Ex groups (= 0.035). White blood cell (WBC), red blood cell (RBC), Hemoglobin (Hgb), and Hematocrit (HCT) in Ac and Ac+400Ex groups showed significant differences from those of the other test groups (
11:10
Acetaminophen-induced liver injury: Molecular mechanism and treatments from natural products. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Front Pharmacol. 2023 ;14:1122632. Epub 2023 Mar 27. PMID: 37050900 Abstract Title: Acetaminophen-induced liver injury: Molecular mechanism and treatments from natural products. Abstract: Acetaminophen (APAP) is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic over-the-counter medicine worldwide. Hepatotoxicity caused by APAP overdose is one of the leading causes of acute liver failure (ALF) in the US and in some parts of Europe, limiting its clinical application. Excessive APAP metabolism depletes glutathione and increases N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimide (NAPQI) levels, leading to oxidative stress, DNA damage, and cell necrosis in the liver, which in turn leads to liver damage. Studies have shown that natural products such as polyphenols, terpenes, anthraquinones, and sulforaphane can activate the hepatocyte antioxidant defense system with Nrf2 as the core player, reduce oxidative stress damage, and protect the liver. As the key enzyme metabolizing APAP into NAPQI, cytochrome P450 enzymes are also considered to be intriguing target for the treatment of APAP-induced liver injury. Here, we systematically review the hepatoprotective activity and molecular mechanisms of the natural products that are found to counteract the hepatotoxicity caused by APAP, providing reference information for future preclinical and clinical trials of such natural products.
11:08
Polyphenol-probiotic-diet may alleviate chronic low-grade inflammation and thus prevent the procession of inflammatory aging. GreenMedInfo
PMID: J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Apr 26 ;71(16):6314-6325. Epub 2023 Apr 14. PMID: 37057839 Abstract Title: Using Inflammatory Biological Age To Evaluate the Preventing Aging Effect of a Polyphenol-Probiotic-Enhanced Dietary Pattern in Adults Aged 50 Years and Older. Abstract: A high-compliance dietary intervention was conducted for 2 weeks in adults aged 50 years and older to investigate the preventing aging effects of a polyphenol-probiotic-enhanced diet (P-diet) by using inflammatory biological age (IBA). Following the P-diet, levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-10, and C-reactive protein were reduced. These effects were accompanied by a significant increase in the richness ofandand decrease in, as well as an increase in butyrate and acetate and decrease in lysine, uracil, and valine. We optimized a model by a back propagation artificial neural network to evaluate the degree of aging, with anof 0.68. After the P-diet intervention, IBA was younger than chronological age and the inflammatory aging potential (age) was observably reduced by 90.12%, with change inage having a direct negative association with. Overall, P-diet may alleviate chronic low-grade inflammation and thus prevent the procession of inflammatory aging.
10:21
Lactobacillus plantarum LP45 inhibits the RANKL/OPG signaling pathway and prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Food Nutr Res. 2023 ;67. Epub 2023 Mar 24. PMID: 37056702 Abstract Title: LP45 inhibits the RANKL/OPG signaling pathway and prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Abstract: OBJECTIVE: To examine the potential effect of the probiotic strainLP45 on osteoporosis and to explore the involved molecular mechanisms.METHODS: A rat model of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIO) was established, which was also orally administered with increasing doses of LP45 for 8 weeks. After the termination of the 8-week treatment, the tibia and femur bones of rats were analyzed for bone histomorphometry, bone mineral content (BMC), and bone mineral density (BMD). Femoral biomechanics were assessed. In addition, levels of osteocalcin, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5 (TRAP5), osteoprotegerin (OPG), and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) in the serum and bone marrow were also measured using ELISA, Western blot, and real time-polymerase chain reaction.RESULTS: GIO caused obvious defects in tibia and femur bone structures, in terms of tissue/bone volume, trabecular separation, trabecular thickness, and trabecular number, which could be rescued by LP45 dose dependently. The GIO-induced reductions in BMC, BMD, osteoblast surfaces per bone surface (BS), as well as elevated osteoclast surface per BS were largely restored by LP45 administration dose-dependently. LP45 also increased femoral biomechanics of GIO rats. Importantly, LP45 dose-dependently restored the changes of osteocalcin, TRAP5, OPG, and RANKL in the serum as well as bone marrow of GIO rats.CONCLUSION: Oral LP45 administration could significantly prevent bone defects in GIO rats, suggesting its potential as a dietary supplement with beneficial effects against osteoporosis, which might involve the RANKL/OPG signaling pathway.
10:15
Lactobacillus plantarum postbiotics trigger AMPK-dependent autophagy to suppress Salmonella intracellular infection and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. GreenMedInfo
PMID: J Cell Physiol. 2023 Jun ;238(6):1336-1353. Epub 2023 Apr 13. PMID: 37052047 Abstract Title: Lactobacillus plantarum postbiotics trigger AMPK-dependent autophagy to suppress Salmonella intracellular infection and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Abstract: We previously found that Lactobacillus plantarum (LP)-derived postbiotics protected animals against Salmonella infection, but the molecular mechanism remains obscure. This study clarified the mechanisms from the perspective of autophagy. Intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC-J2) were pretreated with LP-derived postbiotics (the culture supernatant, LPC; or heat-killed bacteria, LPB), and then challenged with Salmonella enterica Typhimurium (ST). Results showed that LP postbiotics markedly triggered autophagy under ST infection, as indicated by the increased LC3 and Beclin1 and the decreased p62 levels. Meanwhile, LP postbiotics (particularly LPC) exhibited a strong capacity of inhibiting ST adhesion, invasion and replication. Pretreatment with the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) led to a significant decrease of autophagy and the aggravated infection, indicating the importance of autophagy in LP postbiotics-mediated Salmonella elimination. LP postbiotics (especially LPB) significantly suppressed ST-induced inflammation by modulating inflammatory cytokines (the increased interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10, and decreased tumor necrosis factor-(TNF), IL-1, IL-6 and IL-18). Furthermore, LP postbiotics inhibited NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation, as evidenced by the decreased levels of NLRP3, Caspase-1 and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC). Deficits in autophagy resulted in an increase of inflammatory response and inflammasome activation. Finally, we found that both LPC and LPB triggered AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway to induce autophagy, and this was further confirmed by AMPK RNA interference. The intracellular infection and NLRP3 inflammasome were aggravated after AMPK knockdown. In summary, LP postbiotics trigger AMPK-mediated autophagy to suppress Salmonella intracellular infection and NLRP3 inflammasome in IPEC-J2 cells. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of postbiotics, and provide a new strategy for preventing Salmonella infection.
10:00
Walking Backward Boosts Your Memory Articles
Editor's Note: This article is a reprint. It was originally published December 8, 2018.
Researchers from Londons University of Roehampton suggest people who walk backward perform better on memory tests than those who stand still or walk forward. If you are looking to inject new energy into your exercise routine, you might want to try walking or running backward. Beyond the physical benefits to your body, exercising backward may boost your brain power, balance and more.
Walking Backward Shown to Boost Your Memory
In a study published in the journal Cognition,1 researchers from the University of Roehampton (UR) in London have found walking backward can boost your memory. After inviting 114 volunteers to watch a video featuring a woman having her handbag stolen, participants were asked questions about what they saw. Upon completion of the video:
- One subset of the group was asked to walk forward 30 feet (9.1 meters)
- A second subset was told to walk the same distance backward
- People assigned to the control group were told to stand still
Based on their responses to 20 questions about the events in the video, the group that walked backward answered, on average, 10% more of the questions correctly than the control group and those who walked forward. All five variations of the experiment, including one in which the forward or backward movement was simulated, yielded similar effects.
In each scenario, the participants walking backward consistently got the most answers right. These outcomes resulted in the team of researchers, led by Aleksandar Aksentijevic, Ph.D., senior lecturer in psychology at UR, suggesting the experiment is an indication that a link between the concepts of 'time' and 'space' are essential to the way our minds form memories.2
It's a partial vindication of this idea that time is really expressed via space, Aksentijevic told the Daily Mail.3 That said, he suggests more studies are needed to unravel the mysteries of why motion, real or imagined, has the potential to improve our memory.
'I am sure that some of this work could be useful in helping people remember things, but how [that will be possible] is a question [needing] more research, he noted.4
Walking Backward Shown to Improve Cognitive Control, Balance
A 2009 b...
The Wide-Ranging Health Benefits of Niacinamide Articles
In a series of articles, biohacker Georgi Dinkov highlights a variety of benefits of niacinamide (aka nicotinamide), a form of niacin (vitamin B3) that plays a vital role in energy metabolism, as its essential for the mitochondrial electron transport chain to function. Without it, your mitochondria cannot make energy.
Niacinamide is so important because it is a precursor for
Obesity Epidemic Linked to Decline in Basic Metabolic Rate
It does not take much acumen to realize that with double digit declines over a 3-decade period, by now our BMR is probably only half of the BMR of people who lived at the turn of the 20th century, Dinkov writes.3
What makes the situation worse is that if BMR has declined so much, the current guidelines for optimal health reduced caloric intake and plenty of exercise are virtually guaranteed to make the situation even worse since they will invariably further lower the BMR ...
...
Daily Breathing Exercises Could Reduce Heart Attack Risk Articles
Using slow breathing methods to help you relax can lower your blood pressure, thereby reducing your risk of related heart attack, stroke and heart disease. Breathing exercises offer a non-pharmacological method for reducing high blood pressure,1 making them useful for the 1.28 billion people affected by this condition worldwide.2
Among them, about half are unaware that their blood pressure is high. This is why high blood pressure is often referred to as the "silent killer." Often, people dont know their blood pressure is in an unhealthy range until complications occur. Fortunately, breathing exercises can be practiced by anyone, any time, providing a simple way to help manage the condition.
Further, theres no downside to trying them, so theres good reason to give breathing exercises a chance, even if you havent been diagnosed with high blood pressure.
Reduce Blood Pressure With Slow Breathing
Engaging in slow, deep breathing for just two minutes lowers systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 8.6 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) by 4.9 mmHg among people with high blood pressure, according to a 2005 study.3 Slow breathing refers to 10 breaths per minute or less "with prolonged, rhythmic, slow and deep expiratory periods."
This causes biochemical changes that induce relaxation, including increasing endorphins and lowering adrenaline and blood acidity. Slow breathing "increases the length of the diaphragm contraction, minimizes the respiratory rate, and deepens the volume of inspiration and expiration, thus maximizing the amount of oxygen entering the bloodstream," researchers wrote in Frontiers in Physiology, and this is only the beginning.4
The team conducted a scoping review of 20 studies, which also revealed slow breathings blood pressure benefits. They found systolic blood pressure declined by 4 to 54.22 mmHg, while diastolic blood pressure decreased by 3 to 17 mmHg among study participants aged from 18 to 75.5
One way slow breathing works is via its effect on the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Your ANS controls both your bodys sympathetic nervous system (SNS) the part that triggers your "fight-or-flight" response as well as its parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which triggers the relaxation response.
Any type of external stressor everything from an argument with a loved one to a night of lost sleep will prompt a reaction from the ANS, which signals to your brains hypothalamus to either ramp up into overdrive or calm down....
09:55
Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM405 against rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Nutrients. 2023 Apr 1 ;15(7). Epub 2023 Apr 1. PMID: 37049578 Abstract Title: CCFM405 against Rotenone-Induced Parkinson's Disease Mice via Regulating Gut Microbiota and Branched-Chain Amino Acids Biosynthesis. Abstract: Recent studies have demonstrated that disturbances in the gut microbiota and microbiota -derived metabolites contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD), suggesting that probiotic treatments that restore them may delay disease progression. This study aimed to examine the attenuating efficacy ofCCFM405 and the potential mechanisms in mice with rotenone-induced PD. Our results indicate thatCCFM405 ameliorated rotenone-induced motor deficits and constipation, decreased dopaminergic neuronal death, reduced intestinal inflammation and neuroinflammation, and raised dopamine levels, 5-HT, and associated metabolites in the striatal region of the brain in mice with PD. Sequencing of 16S rRNA from fecal microbiota revealed thatCCFM405 normalized the gut bacterial composition in mice with PD, as evidenced by the increased relative abundance of the following genus,,, and, and decreased relative abundance of,,, and. The PICRUSt-predicted gut microbiota function revealed thatCCFM405 enhanced the biosynthesis of amino acid pathways, particularly valine, leucine, and isoleucine (branched-chain amino acids, BCAAs). A non-metabolomic analysis of the serum and feces showed thatCCFM405 markedly increased the levels of BCAAs. Pathway enrichment analysis based on the KEGG database further suggested thatCCFM405 supplementation can promote BCAAs biosynthesis. Collectively,CCFM405 can help to prevent rotenone-induced PD by modulating the gut microbiota-metabolite axis. BCAAs may play a dominant role inCCFM405-associated neuroprotection in PD mice. This probiotic could be utilized as a potential food supplement in the management of PD.
09:52
Neuroprotective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 5 ;24(7). Epub 2023 Apr 5. PMID: 37047769 Abstract Title: Neuroprotective Effects ofPS128 in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease: The Role of Gut Microbiota and MicroRNAs. Abstract: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by motor deficits and marked neuroinflammation in various brain regions. The pathophysiology of PD is complex and mounting evidence has suggested an association with the dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) and gut dysbiosis. Using a rotenone-induced PD mouse model, we observed that administration ofPS128 (PS128) significantly improved motor deficits in PD-like mice, accompanied by an increased level of dopamine, reduced dopaminergic neuron loss, reduced microglial activation, reduced levels of inflammatory factors, and enhanced expression of neurotrophic factor in the brain. Notably, the inflammation-related expression of miR-155-5p was significantly upregulated in the proximal colon, midbrain, and striatum of PD-like mice. PS128 reduced the level of miR-155-5p, whereas it increased the expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1), a direct target of miR-155-5p and a critical inhibitor of the inflammatory response in the brain. Alteration of the fecal microbiota in PD-like mice was partially restored by PS128 administration. Among them,,_6,, andwere statistically correlated with the improvement of rotenone-induced motor deficits and the expression of miR-155-5p and SOCS1. Our findings suggested that PS128 ameliorates motor deficits and exerts neuroprotective effects by regulating the gut microbiota and miR-155-5p/SOCS1 pathway in rotenone-induced PD-like mice.
09:48
L. plantarum JYLP-326 could be an effective strategy to alleviate anxiety, depression, and insomnia in test anxious college students. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Front Immunol. 2023 ;14:1158137. Epub 2023 Mar 23. PMID: 37033942 Abstract Title: PsychobioticJYLP-326 relieves anxiety, depression, and insomnia symptoms in test anxious collegemodulating the gut microbiota and its metabolism. Abstract: INTRODUCTION: Test anxiety is a common issue among college students, which can affect their physical and psychological health. However, effective interventions or therapeutic strategies are still lacking. This study aims to evaluate the potential effects ofJYLP-326 on test anxious college students.METHODS: Sixty anxious students were enrolled and randomly allocated to the placebo group and the probiotic group. Both groups were instructed to take placebo and JYLP-326 products twice per day for three weeks, respectively. Thirty unanxious students with no treatments were assigned to a regular control group. The anxiety, depression, and insomnia questionnaires were used to measure students' mental states at the baseline and the end of this study. 16S rRNA sequencing and untargeted metabolomics were performed to analyze the changes in the gut microbiota and fecal metabolism.RESULTS: The questionnaire results suggested that JYLP-326 administration could relieve the symptoms of anxiety, depression, and insomnia in test anxious students. The gut microbiomes of the placebo group showed a significantly greater diversity index than the control group (p
09:45
Sulforaphane exhibits potent renoprotective effects in preclinical models of kidney diseases. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Life Sci. 2023 Jun 1 ;322:121664. Epub 2023 Apr 5. PMID: 37023957 Abstract Title: Sulforaphane exhibits potent renoprotective effects in preclinical models of kidney diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Abstract: AIMS: Sulforaphane (SFN), a naturally occurring isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables, has received extensive attention as a natural activator of the Nrf2/Keap1 cytoprotective pathway. In this review, a meta-analysis and systematic review of the renoprotective effects of SFN were performed in various preclinical models of kidney diseases.MAIN METHODS: The primary outcome was the impact of SFN on renal function biomarkers (uremia, creatininemia, proteinuria or creatinine clearance) and secondary outcomes were kidney lesion histological indices/kidney injury molecular biomarkers. The effects of SFN were evaluated according to the standardized mean differences (SMDs). A random-effects model was applied to estimate the overall summary effect.KEY FINDINGS: Twenty-five articles (out of 209 studies) were selected from the literature. SFN administration significantly increased creatinine clearance (SMD +1.88 95 % CI: [1.09; 2.68], P
09:43
Anticancer effect and safety of doxorubicin and nutraceutical sulforaphane liposomal formulation in triple-negative breast cancer. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May ;161:114490. Epub 2023 Mar 15. PMID: 36931031 Abstract Title: Anticancer effect and safety of doxorubicin and nutraceutical sulforaphane liposomal formulation in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) animal model. Abstract: Female breast cancer is the most deadly cancer in women worldwide. The triple-negative breast cancer subtype therapies, due to the lack of specific drug targets, are still based on systemic chemotherapy with doxorubicin, which is burdened with severe adverse effects. To enhance therapeutic success and protect against systemic toxicity, drug carriers or combination therapy are being developed. Thus, an innovative liposomal formulation containing doxorubicin and the main nutraceutical, sulforaphane, has been developed. The anticancer efficacy and safety of the proposed liposomal formulation was evaluated in vivo, in a 4T1 mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer, and the mechanism of action was determined in vitro, using triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and non-tumorigenic breast MCF-10A cell line. The elaborated drug carriers were shown to efficiently deliver both compounds into the cancer cell and direct doxorubicin to the cell nucleus. Incorporation of sulforaphane resulted in a twofold inhibition of tumor growth and the potential of up to a fourfold reduction in doxorubicin concentration due to the synergistic interaction between the two compounds. Sulforaphane was shown to increase the accumulation of doxorubicin in the nuclei of cancer cells, accompanied by inhibition of mitosis, without affecting the reactive oxygen species status of the cell. In normal cells, an antagonistic effect resulting in less cytotoxicity was observed. In vivo results showed that sulforaphane incorporation yielded not only cardioprotective, but also nephro- and hepatoprotective effects. The results of the research revealed the prospects of applying sulforaphane as a component of liposomal doxorubicin in triple-negative breast cancer chemotherapy.
09:36
Sulforaphane suppresses paraquat-induced oxidative damage. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Apr 1 ;254:114747. Epub 2023 Mar 10. PMID: 36907095 Abstract Title: Sulforaphane suppresses paraquat-induced oxidative damage in bovine in vitro-matured oocytes through Nrf2 transduction pathway. Abstract: Sulforaphane (SFN), a bioactive phytocompound extracted from cruciferous plants, has received increasing attention due to its vital cytoprotective role in eliminating oxidative free radical through activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2)-mediated signal transduction pathway. This study aims at a better insight into the protective benefit of SFN in attenuating paraquat (PQ)-caused impairment in bovine in vitro-matured oocytes and the possible mechanisms involved therein. Results showed that addition of 1 M SFN during oocyte maturation obtained higher proportions of matured oocytes and in vitro-fertilized embryos. SFN application attenuated the toxicological effects of PQ on bovine oocytes, as manifested by enhanced extending capability of cumulus cell and increased extrusion proportion of first polar body. Following incubation with SFN, oocytes exposed to PQ exhibited reduced intracellular ROS and lipid accumulation levels, and elevated T-SOD and GSH contents. SFN also effectively inhibited PQ-mediated increase in BAX and CASPASE-3 protein expressions. Besides, SFN promoted the transcription of NRF2 and its downstream antioxidative-related genes GCLC, GCLM, HO-1, NQO-1, and TXN1 in a PQ-exposed environment, indicating that SFN prevents PQ-caused cytotoxicity through activation of Nrf2 signal transduction pathway. The mechanisms underlying the role of SFN against PQ-induced injury included the inhibition of TXNIP protein and restoration of the global O-GlcNAc level. Collectively, these findings provide novel evidence for the protective role of SFN in alleviating PQ-caused injury, and suggest that SFN application may be an efficacious intervention strategy against PQ cytotoxicity.
07:47
A single session of Ardha Matsyendrasana for 15 minutes can effectively reduce blood glucose levels in patients with T2DM. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Adv Mind Body Med. 2023 Spring;37(2):5-8. PMID: 37315227 Abstract Title: Effect of a Single Yoga Asana on Blood Glucose Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Self-Controlled Study. Abstract: CONTEXT: Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. Yoga has been shown to have positive effects on blood sugar levels in diabetes patients. However, there is limited research on the effects of specific yoga poses on blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM).OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the effect of a single yoga asana, Ardha Matsyendrasana, on random blood glucose (RBG) levels in patients with T2DM. Specifically, we aimed to investigate whether a 15-minute practice of Ardha Matsyendrasana could reduce RBG levels in patients with T2DM.DESIGN: This study employed a self-controlled design to evaluate the effect of Ardha Matsyendrasana on blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.PARTICIPANTS: 100 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were recruited for this study.INTERVENTIONS: All participants underwent two sessions: a control session (CS) and an asana session (AS), each lasting 15 minutes. During the CS, participants rested in a sitting pose, while during the AS, they practiced Ardha Matsyendrasana. The order of the sessions was randomized, with half the participants undergoing the CS on day 1, the AS on day 2, and the other half undergoing the sessions in reverse order.OUTCOME MEASURES: We measured participants' random blood glucose (RBG) levels immediately before and after each intervention.STATISTICAL ANALYSIS: The statistical package for the compare RBG levels before and after each intervention.RESULTS: The study demonstrated a significant reduction in random blood glucose (RBG) levels in the Ardha Matsyendrasana session compared to the control session. This trend was observed in both males and females with T2DM.CONCLUSIONS: A single session of Ardha Matsyendrasana for 15 minutes can effectively reduce blood glucose levels in patients with T2DM. However, further studies are required to determine the long-term effects of this asana on glycemic control.
07:46
Yoga practice facilitates prefrontal oxygenation and working memory in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Adv Mind Body Med. 2023 Spring;37(2):24-31. PMID: 37315229 Abstract Title: Yoga Practice Facilitates Prefrontal Oxygenation and Working Memory in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Pilot Study. Abstract: BACKGROUND: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with cognitive decline. Lifestyle behaviors such as yoga practices play a significant role in preventing cognitive decline.PURPOSE: The goal of this study was to assess the effect of yoga intervention on working memory and prefrontal cortex (PFC) oxygenation in T2DM patients.METHODS: Twenty T2DM participants, aged between 40 and 60 years, volunteered for a 6-week study. Participants were randomized into a yoga practice (n = 10) and a waitlist control group (n = 10). The n-back task was administered to evaluate working memory before and after the intervention. While performing the working memory task, PFC oxygenation was monitored using functional near-infrared spectroscopy.RESULTS: The yoga group showed a significant improvement in working memory performance. The accuracy improved in 1-back (mean difference of 4.73%, 95% CI[0.69,8.77], P = .026) and 2-back (8.0%, 95% CI[1.89,14.1], P = .016) task conditions. The reaction time improved in 0-back (mean difference of -79.07 milliseconds, 95% CI[-128.3,-29.8]), 1-back (mean difference of -119.17 milliseconds, 95% CI[-217.5,-20.8] ) and 2-back (-76.06 milliseconds, 95% CI[-148.8,-3.3]) task conditions. In the yoga group, at post-intervention, higher oxygenation was observed during 0-back and 1-back task conditions (Beta coefficient mean difference of 211.3, 95% CI[2.8, 420.0], P = .048 and 80.5, 95% CI [3.7,157.2], P = .042 respectively) in the left PFC region compared to the pre-intervention values. The control group showed no significant change in working memory performance and PFC oxygenation.CONCLUSIONS: The study suggests that yoga practice may improve working memory performance and facilitate higher PFC oxygenation in T2DM patients. Further studies with a larger sample and a longer intervention period are required to strengthen the findings.
07:45
Physical and psychological impact of yoga therapy in improving heart failure. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Trop Doct. 2023 Jun 15:494755231180633. Epub 2023 Jun 15. PMID: 37321800 Abstract Title: Physical and psychological impact of yoga therapy in improving heart failure. Abstract: Effective therapy for patients with chronic cardiac failure (CCF) entails significant lifestyle modifications as well as often complex pharmaceutical regimes to alleviate symptoms, which, however, do not actually cure many patients. The gradual loss of cardiac function is impeded but not halted by such complicated pharmacological therapy, which primarily includes angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers and diuretics, and sometimes digoxin, aspirin, warfarin, and anti-arrhythmic agents. Patients may be advised to track their weight and modify their diuretic prescription accordingly to avoid fluid overload or dehydration as part of the treatment plan. Non-pharmacologic treatment options are routinely integrated to improve the management of somatic complaints. Yoga and specialized breathing exercises seem to help CCF patients improve their cardiorespiratory and autonomic system function, and also their quality of life. We present the evidence.
07:36
Efficacy of yoga nidra on depression, anxiety, and insomnia. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Int J Yoga Therap. 2023 Jan 1 ;33(2023). PMID: 37327384 Abstract Title: Efficacy of Yoga Nidra on Depression, Anxiety, and Insomnia in Frontline COVID-19 Healthcare Workers: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Abstract: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a surge of mental health disturbances and the subsequent use of various mind-body therapies. Although evidence supports the benefits of yoga for mental health in a variety of disease states, information on its effects among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 epidemic is scarce. Therefore, this study evaluated and compared the efficacy of relaxation to music and yoga nidra on the mental health of frontline healthcare workers during the pandemic. This open-label randomized trial was conducted at a Level III COVID-19 care center. In the Relaxation-to-Music Group, participants received deep relaxation music, whereas those in the Yoga Nidra Group performed yoga nidra practices; both interventions were delivered through a YouTube platform and were to be done daily for 30 minutes during the healthcare workers' 2-week duty periods. The primary outcomes were measured using scores of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ)-9, Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)-7 scale, and Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) at the end of the duty period. A total of 79 healthcare workers were randomly divided into two groups: (1) Relaxation-to-Music (n = 40) and (2) Yoga Nidra (n = 39). Demographics; clinical characteristics; and PHQ-9, GAD-7, and ISI scores of the two groups were comparable at baseline. In the Yoga Nidra Group, PHQ-9 scores decreased significantly (5.174.25 to 3.032.40, p = 0.002) compared to the Relaxation-to-Music Group (5.684.73 to 4.342.90, p = 0.064). Similarly, GAD-7 scores decreased significantly in the Yoga Nidra Group (4.933.27 to 2.332.56, p
07:35
The effects of yoga and stabilization exercises in patients with chronic low back pain. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Holist Nurs Pract. 2023 Jul-Aug 01;37(4):E59-E68. PMID: 37335153 Abstract Title: The Effects of Yoga and Stabilization Exercises in Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized Crossover Study. Abstract: This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of yoga and stabilization exercises in patients with chronic low back pain. Thirty-five female patients were randomly assigned to the stabilization exercise group or the yoga group. Outcome measures were the visual analog scale (VAS), Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) and Back Performance Scale (BPS), 6-minute walk test (6MWT), Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire (FABQ), and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). The scores of the VAS, ODI, BPS, 6MWT, and PSQI improved significantly after both interventions (P
07:32
The impact of humor therapy on people suffering from depression or anxiety. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Brain Behav. 2023 Jun 21:e3108. Epub 2023 Jun 21. PMID: 37340873 Abstract Title: The impact of humor therapy on people suffering from depression or anxiety: An integrative literature review. Abstract: OBJECTIVES: To identify and synthesize existing research on the effectiveness and feasibility of multiform humor therapy on people suffering from depression or anxiety, with the hope of benefiting future research.METHODS: An integrative literature review of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed studies was performed. The PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, and CINAHL databases were searched up to March 2022. Two independent reviewers conducted each stage of the review process, by assessing eligibility using preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analyses (PRISMA) and quality appraisal using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool, and data extraction.RESULTS: In this integrative review, 29 papers were included, containing 2964 participants across a diverse range of studies, including quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods. The articles were from the United States, Australia, Italy, Turkey, South Korea, Iran, Israel, China, and Germany. The findings indicated that most of the subjects thought humor therapy was effective in improving depression and anxiety while a few participants considered the effect insignificant. However, more high-quality studies will be needed to confirm these conclusions.DISCUSSION: This review collated and summarized findings from studies examining the impact of humor therapy (medical clowns, laughter therapy/yoga) on people with depression or anxiety, including children undergoing surgery or anesthesia, older people in nursing homes, patients with Parkinson's disease, cancer, mental illness, and undergoing dialysis, retired women, and college students. The results from this review may help inform future research, policy, and practice in humor therapy to improve people's symptoms of depression and anxiety.IMPACT: This systematic review objectively evaluated the effect of humor therapy on depression and anxiety. As a simple and feasible complementary alternative therapy, humor therapy may provide a favorable alternative for clinicians, nurses, and patients in the future.
07:23
Vinpocetine mitigates DMH-induce pre-neoplastic colon damage. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jun ;119:110236. Epub 2023 May 5. PMID: 37148772 Abstract Title: Vinpocetine mitigates DMH-induce pre-neoplastic colon damage in rats through inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Abstract: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is currently recognized as the third most prevalent cancer worldwide. Vinpocetine is a synthetic derivative of the vinca alkaloid vincamine. It has been found effective in ameliorating the growth and progression of cancerous cells. However, its pharmacological effect on colon damage remains elusive. Hence, in this study, we have shown the role of vinpocetine in DMH-induced colon carcinogenesis. At first, male albino Wistar rats were administered with DMH consistently for four weeks to induce pre-neoplastic colon damage. Afterward, animals were treated with vinpocetine (4.2 and 8.4 mg/kg/day p.o.) for 15 days. Serum samples were collected to assess the physiological parameters, including ELISA and NMR metabolomics. Colon from all the groups was collected and processed separately for histopathology and western blot analysis. Vinpocetine attenuated the altered plasma parameters; lipid profile and showed anti-proliferative action as evidenced by suppressed COX-2 stimulation and decreased levels of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, and IL-10. Vinpocetine is significantly effective in preventing CRC which may be associated with its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential. Accordingly, vinpocetine could serve as a potential anticancer agent for CRC treatment and thus be considered for future clinical and therapeutic research.
07:19
Effect of vinpocetine alone and in combination with enalapril in experimental model of diabetic cardiomyopathy. GreenMedInfo
PMID: J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023 May 25. Epub 2023 May 25. PMID: 37229596 Abstract Title: Effect of vinpocetine alone and in combination with enalapril in experimental model of diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats: possible involvement of PDE-1/TGF-/ Smad 2/3 signalling pathways. Abstract: OBJECTIVE: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DC) is one of the severe secondary complications of diabetes mellitus in humans. Vinpocetine is an alkaloid having pleiotropic pharmacological effects. The present study is designed to investigate the effect of vinpocetine in DC in rats.METHODS: Rats were fed a high-fat diet for nine weeks along with single dose of streptozotocin after the second week to induce DC. The haemodynamic evaluation was performed to assess the functional status of rats using the Biopac system. Cardiac echocardiography, biochemical, oxidative stress parameters and inflammatory cytokine level were analysed in addition to haematoxylin-eosin and Masson's trichome staining to study histological changes, cardiomyocyte diameter and fibrosis, respectively. Phosphodiesterase-1 (PDE-1), transforming growth factor-(TGF-) and p-Smad 2/3 expression in cardiac tissues were quantified using western blot/RT-PCR.KEY FINDING: Vinpocetine treatment and its combination with enalapril decreased the glucose levels compared to diabetic rats. Vinpocetine improved the echocardiographic parameters and cardiac functional status of rats. Vinpocetine decreased the cardiac biochemical parameters, oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokine levels, cardiomyocyte diameter and fibrosis in rats. Interestingly, expressions of PDE-1, TGF-and p-Smad 2/3 were ameliorated by vinpocetine alone and in combination with enalapril.CONCLUSIONS: Vinpocetine is a well-known inhibitor of PDE-1 and the protective effect of vinpocetine in DC is exerted by inhibition of PDE-1 and subsequent inhibition of the expression of TGF-/Smad 2/3.
07:15
Neuroprotective effects of vinpocetine against ischemia-reperfusion injury, GreenMedInfo
PMID: Neuroscience. 2023 Jun 7. Epub 2023 Jun 7. PMID: 37290685 Abstract Title: Neuroprotective Effects of Vinpocetine Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway. Abstract: Ischemic stroke is one of the main causes of serious disability and death worldwide. NLRP3 inflammasome is an intracellular pattern recognition receptor composed of polyprotein complex, which participates in mediating a series of inflammatory responses and is considered as a potential target for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Vinpocetine, a derivative of vincamine, has been widely used in the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke. However, the therapeutic mechanism of vinpocetine is not clear, and its effect on NLRP3 inflammasome remains to be determined. In this study, we used the mouse model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) to simulate the occurrence of ischemic stroke. Different doses of vinpocetine (5, 10, 15mg/kg/d) were injected intraperitoneally for 3days after ischemia-reperfusion in mice. The effects of different doses of vinpocetine on the degree of ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice were observed by TTC staining and modified neurological severity score scale, and the optimal dose was determined. Then, based on this optimal dose, we observed the effects of vinpocetine on apoptosis, microglial proliferation and NLRP3 inflammasome. In addition, we compared the effects of vinpocetine and MCC950 (a specific inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome) on NLRP3 inflammasome. Our results show that vinpocetine can effectively reduce the infarct volume and promote the recovery of behavioral function in stroke mice, and the maximal beneficial effects were observed at the dose of 10mg/kg/d. Vinpocetine can effectively inhibit the apoptosis of peri-infarct neurons, promote the expression of Bcl-2, inhibit the expression of Bax and Cleaved Caspase-3, and reduce the proliferation of peri-infarct microglia. In addition, vinpocetine, like MCC950, can reduce the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome. Therefore, vinpocetine can effectively alleviate the ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice, and the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome may be an important therapeutic mechanism of vinpocetine.
07:14
Antidepressants Permanently Destroyed My Sex Life Mad In America
From The Telegraph: More than eight million people in England are on antidepressants, but with devastating side effects for some, are they being prescribed too freely?

***
Back to Around the Web
The post Antidepressants Permanently Destroyed My Sex Life appeared first on Mad In America.
07:05
New insights on the potential effect of vinpocetine in Parkinson's disease. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Jun 19. Epub 2023 Jun 19. PMID: 37335452 Abstract Title: New insights on the potential effect of vinpocetine in Parkinson's disease: one of the neglected warden and baffling topics. Abstract: Vinpocetine (VPN) is an ethyl apovincaminate that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects by inhibiting the expression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B) and phosphodiesterase enzyme 1 (PDE-1). VPN is used in the management of stroke, dementia, and other neurodegenerative brain diseases. VPN may be effective in treating Parkinson's disease (PD). Therefore, this review aimed to clarify the mechanistic role of VPN in the management of PD. VPN has protective and restorative effects against neuronal injury by reducing neuroinflammation, and improvement of synaptic plasticity and cerebral blood flow. VPN protects dopaminergic neurons by reducing oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, glutamate neurotoxicity, and regulation of Caoverloads. VPN can alleviate PD neuropathology through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiapoptotic and neurogenic effects. VPN through inhibition of PDE1 improves cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) signaling in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra (SN). VPN improves PD neuropathology through PDE1 inhibition with a subsequent increase of the cAMP/cGMP signaling pathway. Therefore, increasing cAMP leads to antioxidant effects, while augmentation of cGMP by VPN leads to anti-inflammatory effects which reduced neurotoxicity and development of motor severity in PD. In conclusion, this review indicated that VPN could be effective in the management of PD.
06:52
Crosstalk between dietary pomegranate and gut microbiota: evidence of health benefits. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 19:1-27. Epub 2023 Jun 19. PMID: 37335106 Abstract Title: Crosstalk between dietary pomegranate and gut microbiota: evidence of health benefits. Abstract: Gut microbiota (GM) is an invisible organ that plays an important role in human health. Increasing evidence suggests that polyphenols in pomegranate (punicalagin, PU) could serve as prebiotics to modulate the composition and function of GM. In turn, GM transform PU into bioactive metabolites such as ellagic acid (EA) and urolithin (Uro). In this review, the interplay between pomegranate and GM is thoroughly described by unveiling a dialog in which both actors seem to affect each other's roles. In a first dialog, the influence of bioactive compounds from pomegranate on GM is described. The second act shows how the GM biotransform pomegranate phenolics into Uro. Finally, the health benefits of Uro and that related molecular mechanism are summarized and discussed. Intake of pomegranate promotes beneficial bacteria in GM (e.g.spp.,spp.) while reducing the growth of harmful bacteria (e.g.group,)., andspp., among others, biotransform PU and EA into Uro. Uro contributes to strengthening intestinal barrier and reducing inflammatory processes. Yet, Uro production varies greatly among individuals and depend on GM composition. Uro-producing bacteria and precise metabolic pathways need to be further elucidated therefore contributing to personalized and precision nutrition.
06:51
In silico molecular study of hepatitis B virus X protein as a therapeutic target. GreenMedInfo
PMID: J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 May 30:1-14. Epub 2023 May 30. PMID: 37254310 Abstract Title: In silico molecular study of hepatitis B virus X protein as a therapeutic target. Abstract: The Hepatitis B virus is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. HBx viral protein is considered a contributor to pathogenesis and hepatocarcinogenesis. This study aimed to screen the effect of some antiviral compounds to target HBx protein for inhibition of its function. Here, molecular docking, molcular dynsmic simulation, MM/GBSA and T-SNE methods were applied to study the complex stability and to cluster the conformations that generated in the simulation. Among the 179 compounds screened in this study, three antiviral agents (SC75741, Punicalagin, and Ledipasvir) exhibited the lowest docking energy and best interaction. Among these compounds, SC75741 was identified as a potent inhibitor of HBx that showed the best and most stable interaction during molecular dynamic simulation, and blocking a region near to HBx helix resides (aa 88-100) that is associated with cell invasion. The analysis of relative binding free energy through MM/GBSA for molecular dynamic simulation results revealed binding energy -9.9kcal/mol for SC75741, -11kcal/mol for Punicalagin, and -10.1kcal/mol for Ledipasvir. These results elucidate the possible use of these compounds in the research for targeting HBx.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
06:48
The role of punicalagin and its metabolites in atherosclerosis. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 9 ;24(10). Epub 2023 May 9. PMID: 37239823 Abstract Title: The Role of Punicalagin and Its Metabolites in Atherosclerosis and Risk Factors Associated with the Disease. Abstract: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ACVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. Although current therapies, such as statins, have led to a marked reduction in morbidity and mortality from ACVD, they are associated with considerable residual risk for the disease together with various adverse side effects. Natural compounds are generally well-tolerated; a major recent goal has been to harness their full potential in the prevention and treatment of ACVD, either alone or together with existing pharmacotherapies. Punicalagin (PC) is the main polyphenol present in pomegranates and pomegranate juice and demonstrates many beneficial actions, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-atherogenic properties. The objective of this review is to inform on our current understanding of the pathogenesis of ACVD and the potential mechanisms underlying the beneficial actions of PC and its metabolites in the disease, including the attenuation of dyslipidemia, oxidative stress, endothelial cell dysfunction, foam cell formation, and inflammation mediated by cytokines and immune cells together with the regulation of proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Some of the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of PC and its metabolites are due to their strong radical-scavenging activities. PC and its metabolites also inhibit the risk factors of atherosclerosis, including hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, inflammation, hypertension, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Despite the promising findings that have emerged from numerous in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies, deeper mechanistic insights and large clinical trials are required to harness the full potential of PC and its metabolites in the prevention and treatment of ACVD.
06:45
Punicalagin inhibits hepatic lipid deposition in obesity. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Apr ;48(7):1751-1759. PMID: 37282949 Abstract Title: [Punicalagin inhibits hepatic lipid deposition in obese mice via AMPK/ACC pathway]. Abstract: Hepatic lipid deposition is one of the basic manifestations of obesity, and nowadays pharmacological treatment is the most important tool. Punicalagin(PU), a polyphenol derived from pomegranate peel, is a potential anti-obesity substance. In this study, 60 C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into a normal group and a model group. After establishing a model of simple obesity with a high-fat diet for 12 weeks, the successfully established rat models of obesity were then regrouped into a model group, an orlistat group, a PU low-dose group, a PU medium-dose group, and a PU high-dose group. The normal group was kept on routine diet and other groups continued to feed the high-fat diet. The body weight and food intake were measured and recorded weekly. After 8 weeks, the levels of the four lipids in the serum of each group of mice were determined by an automatic biochemical instrument. Oral glucose tole-rance and intraperitoneal insulin sensitivity were tested. Hemoxylin-eosin(HE) staining was applied to observe the hepatic and adipose tissues. The mRNA expression levels of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor(PPAR) and C/EBPwere determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction(Q-PCR), and the mRNA and protein expression levels of adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase(AMPK), anterior cingulate cortex(ACC), and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A(CPT1A) were determined by Western blot. Finally, the body mass, Lee's index, serum total glyceride(TG), serum total cholesterol(TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol(LDL-C) levels were significantly higher and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(HDL-C) levels were significantly lower in the model group as compared with the normal group. The fat deposition in the liver was significantly increased. The mRNA expression levels of hepatic PPARand C/EBPand the protein expression level of ACC were increased, while the mRNA and protein expression levels of CPT-1(CPT1A) and AMPK were decreased. After PU treatment, the above indexes of obese mice were reversed. In conclusion, PU can decrease the body weight of obese mice and control their food intake. It also plays a role in the regulation of lipid metabolism and glycometabolism metabolism, which can significantly improve hepatic fat deposition. Mechanistically, PU may regulate liver lipid deposition in obese mice by down-regulating lipid synthesis and up-regulating lipolysis through activation of the AMPK/ACC pathway.
06:42
Punicalagin alleviates the hyperproliferation of keratinocytes in psoriasis. GreenMedInfo
PMID: J Nat Med. 2023 Jun 12. Epub 2023 Jun 12. PMID: 37306932 Abstract Title: Punicalagin alleviates the hyperproliferation of keratinocytes in psoriasis through inhibiting SKP2 expression. Abstract: Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by abnormal keratinocytes proliferation and multiple immune cells infiltration in the dermis and epidermis. Although most psoriasis-related researches have been concentrated on the interleukin-23 (IL-23)/interleukin-17 (IL-17) axis, new data suggest that keratinocytes also play a pivotal role in psoriasis. Previously, we found that punicalagin (PUN), a bioactive ellagitannin extracted from Pericarpium Granati (the pericarpium of Punica granatum L.), exerts a therapeutic effect on psoriasis. However, the underlying mechanism, especially its potential modulatory effect on keratinocytes, remains obscure. Our study aims to reveal the potential regulatory effect and its underlying cellular mechanism of PUN on the hyperproliferation of keratinocytes. We used tumor necrosis factor(TNF-), IL-17A and interleukin-6 (IL-6) to induce abnormal proliferation of HaCaT cells (Human Keratinocytes Cells) in vitro. Then, we evaluated the effects of PUN through MTT assay, EdU staining and cell cycle detection. Finally, we explored the underlying cellular mechanisms of PUN via RNA-sequencing, WB in vitro and in vivo. Here, we found that PUN can directly and dose-dependently decrease TNF-, IL-17A and IL-6-induced abnormal proliferation of HaCaT cells in vitro. Mechanically, PUN suppresses the hyperproliferation of keratinocytes through repressing S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) expression in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, overexpression of SKP2 can partly abolish PUN-mediated inhibition of aberrantly proliferative keratinocytes. These results illustrate that PUN can reduce the severity of psoriasis through directly repressing SKP2-mediated abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes, which gives new insight into the therapeutic mechanism of PUN on psoriasis. Moreover, these findings imply that PUN might be a promising drug candidate for the treatment of psoriasis.
06:39
In a Tipsters Note, a View of Science Publishings Achilles Heel Retraction Watch
On paper, data scientist Gunasekaran Manogaran has had a stellar scientific career. He earned an award as a young researcher from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and landed a series of postdoctoral and visiting researcher positions at universities in the U.S, including the University of California, Davis; Gannon University in Pennsylvania; and Howard University in Washington, D.C. His h-index a measure of a researchers impact and productivity is 60, a number that by one model would mark him as truly unique if achieved within 20 years. He did it in fewer than 10.
Emails obtained by Undark, however, suggest some researchers have doubts about his publishing record. The correspondence includes an initial message from someone claiming to have previously worked with Manogaran. It was sent to some 40 editors of scientific journals, many owned by major scientific publishers: Elsevier, Springer Nature, Wiley, and Taylor & Francis among them.
The sender alleges that Manogaran and others run a research paper publishing scam one that both generates revenues and artificially burnishes the scientific bona fides of individual and institutional participants. In particular, the alleged scheme targets what are known in the scientific publishing industry as special issues self-contained special editions that are not part of a journals regular publishing schedule, typically focused on a single topic or theme.
The email, dated April 12, 2022, informs the journal editors that they may have partnered with members of this alleged scheme and urges them to take action. If you dont do that there would be a next group doing the same scam in name of different persons, the email states.
Read the rest of this Retraction Watch-Undark story here.
Like Retraction Watch? You can make a ...
06:34
Neuroprotective effects of vinpocetine in a model of Alzheimer's disease. GreenMedInfo
PMID: BMC Neurosci. 2023 Mar 16 ;24(1):20. Epub 2023 Mar 16. PMID: 36927298 Abstract Title: Neuroprotective effects of vinpocetine, as a phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitor, on long-term potentiation in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Abstract: BACKGROUND: Vinpocetine (Vin) is known as a phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitor (PDE1-I) drug with multilateral effects, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. In this research, we investigated the neuroprotective and therapeutic effects of Vin through hippocampal synaptic plasticity on a rat's model of Alzheimer's disease (AD) induced by an intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of beta-amyloid (A).METHODS: Sixty adult male Wistar rats were randomly divided into six groups: 1. control, 2. sham, 3. A, 4. pretreatment (Vin+A): Vin (4 mg/kg, gavage) for 30 days and then, inducing an AD model by an ICV injection of A(1-42), 5. treatment (A+Vin): inducing an AD model and then receiving Vin for 30 days by gavage, and 7. pretreatment+treatment (Vin+A+Vin): receiving Vin by gavage for 30 days before and 30 days after the induction of an AD model. After these procedures, via stereotaxic surgery, the stimulating electrodes were placed at the perforant pathway (PP) and the recording electrodes were implanted in the dentate gyrus.RESULTS: Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) slope and population spike (PS) amplitude in the Agroup meaningfully diminished compared to the control group after the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP).CONCLUSIONS: Vin could significantly prevent the Aeffects on LTP. It can be concluded that pretreatment and treatment with Vin can be neuroprotective against harmful consequences of Aon hippocampal synaptic plasticity.
06:32
Vinpocetine's potencies ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023 Jan ;26(1):13-22. PMID: 36594060 Abstract Title: Vinpocetine's immunomodulating, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, ant-ifibrotic, and PDE inhibiting potencies ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Abstract: OBJECTIVES: Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a global health problem with a high economic burden. Intratracheal administration of bleomycin is the best model that resembles the pathogenesis of PF in humans. Recently, vinpocetine proved to have neuroprotective, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, anti-aging, and antifibrotic effects through its anti-oxidant, immunomodulating, and anti-inammatory activities. The present study investigated the antifibrotic potentiality of vinpocetine in a rat model of PF induced by intratracheal bleomycin administration.MATERIALS AND METHODS: PF induced by a single intratracheal instillation of 5 mg/kg bleomycin in nine-week-old Wister rats. Oral vinpocetine was used at doses of 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg to treat PF for 21 days immediately after the bleomycin instillation.RESULTS: Vinpocetine dose-dependently ameliorates PF induced by bleomycin administration since vinpocetine effectively restored the normal body weight gain rates, pulmonary architecture, and collagen fiber distribution and suppressed the elevated BALF cell count, lymphocytes and neutrophils percentage, BALF, IL-6, TNF-, and TGF-1 levels and LDH activity, lung tissue MDA level, PDE activity, hydroxyproline content, immunohistochemical expression of-SMA and CD68 positive macrophage, and fibrosis score. Meanwhile, it efficiently augmented the reduced BALF macrophage percentage, IL-10 level, lung tissue GSH level, CAT, and SOD activities.CONCLUSION: Vinpocetine may propose a new promising agent to manage PF.
06:29
Punicalagin protects against impaired skeletal muscle function in high-fat-diet-induced obesity. GreenMedInfo
PMID: Food Funct. 2023 Apr 3 ;14(7):3126-3138. Epub 2023 Apr 3. PMID: 36929898 Abstract Title: Punicalagin protects against impaired skeletal muscle function in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice by regulating TET2. Abstract: The function of skeletal muscles can be markedly hampered by obesity. Ten-eleven translocation 2 (TET2) is an important therapeutic target for ameliorating skeletal muscle dysfunction. Our previous study revealed that punicalagin (PUN) regulated TET2 in obese mice; however, whether PUN can prevent obesity-induced skeletal muscle dysfunction by regulating TET2 remains unclear. In the present study, 40 male C57BL/6J mice were divided into four groups (= 10 per group): the control (CON) group, the high-fat-diet (HFD, negative control) group, the resveratrol (positive control) group, and the PUN group. The ratio of gastrocnemius weight to body weight (0.00970.00160.00800.0011), the grip strength (120.04 g11.1098.89 g2.79), and the muscle fiber count (314.56 per visual field92.73236.44 per visual field50.58) in the PUN group were higher than those in the HFD group. Moreover, the levels of the TET2 protein, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), and 5-formylcytosine (5fC) in skeletal muscles were significantly lower in the HFD group than those in the CON group; these levels increased after PUN treatment. Compared with the HFD group, the phosphorylation level of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)in the PUN group was higher, which effectively enhanced the stability of the TET2 protein. Besides, the ratio of (succinic acid + fumaric acid)/-ketoglutarate in the PUN group was lower than that in the HFD group (43.2112.4299.1937.07), and a lower ratio led to a higher demethylase activity of TET2 in the PUN group than in the HFD group. This study highlights that PUN supplementation protects against obesity-induced impairment of the skeletal muscle functionregulating the protein stability of TET2 and the enzymatic activity of TET2 demethylation.
05:54
Why critics do not sue Robert F Kennedy Jr for defamation Skeptical Raptor
The Skeptical Raptor, stalking pseudoscience in the internet jungle.
Professor Dorit Rubinstein Reiss reviews why the critics of Robert F Kennedy Jr have not sued him for defamation despite his false claims.
05:52
Biometric National Digital IDs are Coming Soon to Pave the Way for Central Bank Digital Currencies Medical Kidnap


by Brian Shilhavy
Editor, Health Impact News
Imagine a world where you cannot purchase anything in a retail store, or online, or be able to access the cash in your bank account, unless you first use your cell phone to scan your face to prove your identity.
You are assured that your face image is secure and never shared or sold to third party advertisers, but now every time you scan your face to make a financial transaction, a new digital image of your face is stored somewhere, where it can be hacked or sold to the highest bidder.
Now, every time you go out into the public where there are cameras everywhere today, from your neighbors door cameras to the cameras on street lights and traffic signals, to even the cameras in and around your car, someone with the technological know-how could literally trace every step you make, and everywhere you went, who you met, and possibly even everything you said and did with that person, because your national ID is now tied into your face scan which you have to constantly use with your national digital ID.
Does this sound like some futuristic science fiction movie? Because I assure you, it is not, and if you do not prepare yourself for the push to give up your biometric data, such as face scans, palm scans, and iris scans to obtain a National ID that will soon be required to participate in the economy, even when purchasing and doing banking online, then you will probably be completely helpless to resist when it comes.
And its coming soon, very soon, as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the Bank of England are already testing such a system, as is the U.S.
Digital IDs will Precede CBDCs

Digital IDs will precede the adoptions of Central Bank Digital Currencies, and it was announced yesterday that UK payments and self-sovereign identity firm Nuggets has developed a digital wallet solution for the retail market and a UK Central Bank Digital Currency.
UK financial authorities work with industry on digital ID, US regulator signals support
UK payments and self-sovereign identity firm Nuggets has worked on developing a digital wallet solution for a retail use case of a potential UK Central Bank Digital Currency.
like the U.S. dollar or the Eur...
05:51
Biometric National Digital IDs are Coming Soon to Pave the Way for Central Bank Digital Currencies Vaccine Impact


by Brian Shilhavy
Editor, Health Impact News
Imagine a world where you cannot purchase anything in a retail store, or online, or be able to access the cash in your bank account, unless you first use your cell phone to scan your face to prove your identity.
You are assured that your face image is secure and never shared or sold to third party advertisers, but now every time you scan your face to make a financial transaction, a new digital image of your face is stored somewhere, where it can be hacked or sold to the highest bidder.
Now, every time you go out into the public where there are cameras everywhere today, from your neighbors door cameras to the cameras on street lights and traffic signals, to even the cameras in and around your car, someone with the technological know-how could literally trace every step you make, and everywhere you went, who you met, and possibly even everything you said and did with that person, because your national ID is now tied into your face scan which you have to constantly use with your national digital ID.
Does this sound like some futuristic science fiction movie? Because I assure you, it is not, and if you do not prepare yourself for the push to give up your biometric data, such as face scans, palm scans, and iris scans to obtain a National ID that will soon be required to participate in the economy, even when purchasing and doing banking online, then you will probably be completely helpless to resist when it comes.
And its coming soon, very soon, as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the Bank of England are already testing such a system, as is the U.S.
Digital IDs will Precede CBDCs

Digital IDs will precede the adoptions of Central Bank Digital Currencies, and it was announced yesterday that UK payments and self-sovereign identity firm Nuggets has developed a digital wallet solution for the retail market and a UK Central Bank Digital Currency.
UK financial authorities work with industry on digital ID, US regulator signals support
UK payments and self-sovereign identity firm Nuggets has worked on developing a digital wallet solution for a retail use case of a potential UK Central Bank Digital Currency.
like the U.S. dollar or the Eur...
05:18
Biometric National Digital IDs are Coming Soon to Pave the Way for Central Bank Digital Currencies Health Impact News


by Brian Shilhavy
Editor, Health Impact News
Imagine a world where you cannot purchase anything in a retail store, or online, or be able to access the cash in your bank account, unless you first use your cell phone to scan your face to prove your identity.
You are assured that your face image is secure and never shared or sold to third party advertisers, but now every time you scan your face to make a financial transaction, a new digital image of your face is stored somewhere, where it can be hacked or sold to the highest bidder.
Now, every time you go out into the public where there are cameras everywhere today, from your neighbors door cameras to the cameras on street lights and traffic signals, to even the cameras in and around your car, someone with the technological know-how could literally trace every step you make, and everywhere you went, who you met, and possibly even everything you said and did with that person, because your national ID is now tied into your face scan which you have to constantly use with your national digital ID.
Does this sound like some futuristic science fiction movie? Because I assure you, it is not, and if you do not prepare yourself for the push to give up your biometric data, such as face scans, palm scans, and iris scans to obtain a National ID that will soon be required to participate in the economy, even when purchasing and doing banking online, then you will probably be completely helpless to resist when it comes.
And its coming soon, very soon, as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the Bank of England are already testing such a system, as is the U.S.
Digital IDs will Precede CBDCs
...
03:00
Splitting Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder Mad In America
Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (C-PTSD) has long been hailed as a beacon of hope in the maze of psychiatric diagnoses, even among those of us who have felt harmed by such labels. It offers a fresh perspective on the relentless, pervasive trauma that acts more as a sculptor than an eventa relentless chiseler that etches seemingly indelible patterns and erects defensive fortresses so deeply embedded in our being that they seem less like experiences weve weathered, and more like integral fragments of our identity.
When ICD-11, the diagnostic manual used by Europe and half the world, recently acknowledged C-PTSD, it was perceived as a potential breakthrough for those of us profoundly impacted by such trauma. Expectations were high for increased understanding, empathy, and support. However, the rapidly changing landscape suggests that the recognition of C-PTSD might be a double-edged sword, inadvertently further marginalizing the very individuals it aimed to assistthose diagnosed with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD). Why?

The Emergence of C-PTSD
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a diagnostic categor...
01:11
CDC Chief Walensky Trivializes VAERS Age of Autism The Rebel Alliance!
Exchange between Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA) and CDC
Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky.
WATCH: Full exchange between Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA) and CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky.
Dr. Walensky: "I'd be happy to have our staff educate your staff."
Rep. Green: "I don't want my staff educated. You should educate the American people about what you've done."
This brings back memories of former CDC head, Dr. Julie Gerberding (SEE 3.25 on VIDEO from Mar 29, 2008 with Sanjay Gupta). One thing is ALWAYS FOR SURE, the head of the CDC will defend vaccines and never honestly address the damage they cause.
C-Span Video With Dr. Walensky and Rep Marjorie Taylor Green Notice how Dr. Walensky trivializes VAERS reports with her example of getting hit by a truck, while she completely ignores Rep. Taylor Greenes comments about myocarditis, deaths, miscarriages and stillbirths associated with the COVID19 vaccine.
Its all meaningless however. After 20 years of watching hearings where officials are called to testify, I can say without a moments hesitation that everyone just goes home afterwards. There will be no press coverage. No further inquiry. Walensky knows this, and it probably accounts for her very smug smile at the end.
June 13, 2023, Exchange between Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA) and CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky
Rep. Taylor Greene: Dr. Walensky, youre coming to the end of your tenure as the CDC director which you stated in January of 2021.
We heard you say today that the COVID19 vaccines are safe and effective.
But what Id like to talk to you today about is the 1.5 million VAERS reports that also reported 35,000 deaths associate...
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day
Wednesday, 21 June
23:05
What is the God Spot? Do we really have one? Chipur
Humans have sought relationships with deities from the beginning of time. Makes you wonder if were wired for it. Have you ever heard of the God Spot? Do we really have one? Lets take a look
The post What is the God Spot? Do we really have one? first appeared on Chipur.
12:36
Andrew John Rugg-Gunn named 2023 recipient of IADR Gold Medal Fluoride Action Network
Alexandria, VA, USA The International Association for Dental Research (IADR) has announced Andrew John Rugg-Gunn as the 2023 recipient of the IADR Gold Medal. Rugg-Gunn, from the Borrow Foundation, Hampshire, England, was recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 101st General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 9th Meeting of the Latin American Region and the 12th World Congress on Preventive Dentistry, that took place on June 21, 2023, in Bogot, Colombia.
Rugg-Gunn has had a major influence on the recognition of the impact of diet and oral health with his service on the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN), his advice and influence on WHO policy, and his influential role in pediatric dentistry in the promotion of fluorides.
As head of the department of Child Dental Health, within Newcastle University during the late 1990s, Rugg-Gunn influenced the careers of scientists within the department and dental school. Two of these went on to become IADR Presidents Paula Moynihan and Angus Walls.
For the past 30+ years, Rugg-Gunn has had an advisory role with the World Health Organization (WHO). He served as an advisor regarding revisions of Oral Health Surveys, Basic Methods (now in its 5th edition), and the revision of Fluorides and Oral health (Technical Report, 1994), published in 2016. He also co-authored the WHO publication Milk Fluoridation for the Prevention of Dental Caries, (2009), and two WHO documents on early childhood caries. Additionally, he was part of a WHO team invited to Beijing in 2000 by the Chinese Ministry of Health to advise on national fluoride policy.
The IADR Gold Medal is the highest recognition bestowed by the IADR. It is presented to a previous recipient of an IADR Distinguished Scientist Award who later builds on their original scientific achievements to more broadly impact science, health research, or population health through the expansion of their field into other disciplines, or through higher administrative positions in academia, government, non-profit, or private industry.
About IADR
The International Association for Dental Research (IADR) is a nonprofit organization with a mission to drive dental, oral, and craniofacial research for health and well-being worldwide. IADR represents the individual scientists, clinician-scientists, dental professionals, and students based in academic, government, non-profit and private-sector institutions who share our mission. Learn more at www.iadr.org.
*Original full-text article online at: https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/992454
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day
Tuesday, 20 June
12:46
Fluoridation could distract from other oral health issues Fluoride Action Network
MHK fears adding substance to drinking water would mean less emphasis on other dental factors
Adding fluoride to the Islands drinking water could distract from other aspects of oral health.
Thats the fear of one of the members of a Tynwald committee thats investigated dental issues among Manx children.
The committee initially suggested a twice-yearly fluoride varnish for children, but the Council of Ministers put forward an amendment seeking a study into fluoridation instead.
With the Manx parliament set to vote on the issue at this months sitting, Garff MHK Daphne Caine says its not the solution to all dental problems:
*Original full-text article online at: https://www.manxradio.com/news/isle-of-man-news/fluoridation-could-distract-from-other-oral-health-issues/
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day
Monday, 19 June
16:10
Go Back:30 Days | 7 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day
Wednesday, 14 June
Sunday, 11 June
16:27
From Oncology to Spirituality: New York Doctor Used Sound Therapy to Heal Cancer Patients AltHealthWorks.com

The late Dr. Mitchell Gaynor with a crystal healing bowl. He used the sounds of these special bowls to soothe and heal cancer patients.